Infamous End Of Lugalzagesi – Ambitious King Who United Sumer
A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com - Lugalzagesi was a Sumerian king who reigned c. 2341 BC - 2316 BC and lived in the mid-fourteenth century BC.
According to his inscriptions, he came to power as the 'ensi' of the Umma city that reached its zenith c. 2275 BC. A royal inscription states that his father, Bubu, was the previous 'ensi' of Umma.
In the Sumerian King List, he is mentioned as the king of the Third Dynasty of Uruk with a reign of 25 years; however, chronology regarding his rule is somewhat uncertain.
He was also the high priest of Nisaba, the Sumerian goddess of writing, learning, harvest, and the patroness of scribes; she was worshiped in sanctuaries and shrines at Umma. Lugalzagesi, who united all Sumer city-states and conquered many foreign countries, called himself "King of all nations."
His reign lasted 25-34 years, depending on which version of the Sumerian king list is correct.
Undoubtedly, it was an outstanding achievement to unite the Sumerian city-states, and it was not an easy task. These city-states had a tradition of independence and were frequently at war.
Most attempts to unite Sumer had failed until Lugalzagesi, a strong ruler, an ambitious and military-minded 'ensi' from neighboring Umma, appeared on the scene, and he could unite the cities of Sumer. In the long-lasting conflict between Umma and Lagash, Lugalzagesi inflicted a severe defeat on the rival town and managed to win supremacy over the whole country as king of Uruk.
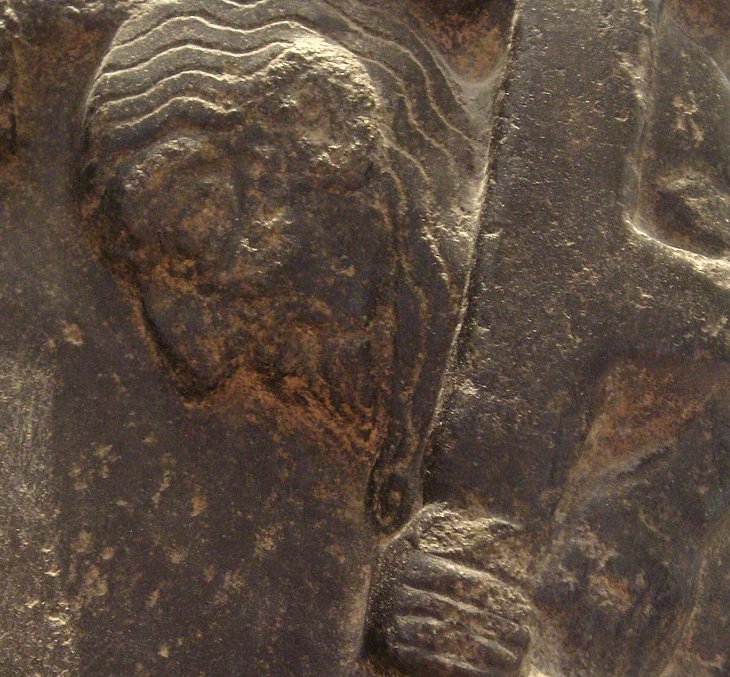 Governor of Umma, King of Uruk, King of the Land. Prisoner in a cage, probably king Lugalzagesi of Uruk due to his oversize figure, being hit on the head with a mace by Sargon of Akkad. Akkadian Empire victory stele circa 2300 BCE. Louvre Museum. Image credit: ALFGRN - CC BY-SA 2.0
Governor of Umma, King of Uruk, King of the Land. Prisoner in a cage, probably king Lugalzagesi of Uruk due to his oversize figure, being hit on the head with a mace by Sargon of Akkad. Akkadian Empire victory stele circa 2300 BCE. Louvre Museum. Image credit: ALFGRN - CC BY-SA 2.0
The union of Sumerians by Lugalzagesi had a very high price. He attacked and besieged neighboring Girsu, the second major city of the kingdom of Lagash, and his war with Urukagina, King of Lagash, was extremely cruel.
The destruction of Lagash city was Lugalzagesi's revenge for the long-lasting humiliation of Umma, though his initial attacks against Lagash were unsuccessful. He was involved in the 150-year-long conflict with Lagash for a fertile plain of Gu-Edin ('Guedena'), a fertile plain mentioned in the Stele of the Vultures, the oldest known historical document. This stele has a long inscription in the Sumerian language that confirms the recurring conflict between the neighboring city-states of Lagash and Umma. It also informs about the victory of Eannatum, king of Lagash.
His reliefs covering the two faces of the stele inform that he burned, looted, and destroyed practically all the holy places of Lagash.
These vicious deeds of Lugalzagesi are recorded in a remarkable document written by a Lagashite scribe and theologian, no doubt at the behest of Urukagina, who – there is reason to believe – survived the catastrophe.
An ancient source (a lamentation) says that Lugalzagesi launched a devastating attack and destroyed Lagash:
"The ruler of Umma has set fire to the temple of Antasura; he has carried away the silver and the lapis lazuli… He has shed blood in the temple of the goddess Nanshe; he has carried away the precious metal and precious stones.
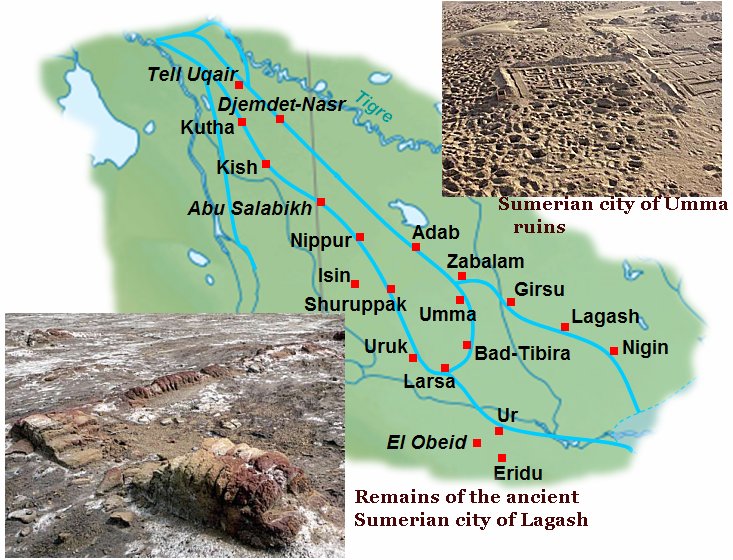
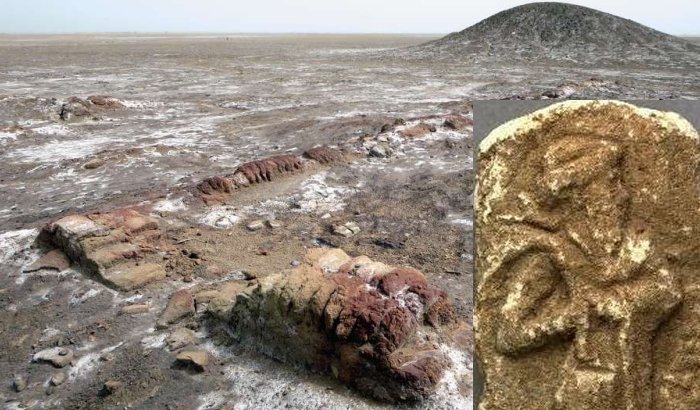 Left: "Mudbrick foundations and a ziggurat are among the remains of the 3rd millennium BC Sumerian city-state of Lagash (Tell al Hiba) northeast of Nasiriyah, Iraq." source; Right: Urukagina, an illegitimate and controversial claimant to power, the last king of the first dynasty of Lagash who came to power divinely - as he claimed - when Ningirsu, warrior of Enlil, granted him the kingship of Lagash.
Left: "Mudbrick foundations and a ziggurat are among the remains of the 3rd millennium BC Sumerian city-state of Lagash (Tell al Hiba) northeast of Nasiriyah, Iraq." source; Right: Urukagina, an illegitimate and controversial claimant to power, the last king of the first dynasty of Lagash who came to power divinely - as he claimed - when Ningirsu, warrior of Enlil, granted him the kingship of Lagash.
The Man of Umma has committed a sin against the god Ningirsu… May, the hand that he dared to raise against Ningirsu be cut off. There was no fault in Urukagina, King of Lagash. May Nisaba, the goddess of Lugalzagesi, ruler of Umma, make him bear his mortal sin upon his neck." 1
These prophetic words were finally fulfilled, but it took time before they happened.
In the meantime, in addition to Lagash, Lugalzagesi also overcame Kish, Ur, Nippur, Larsa, and Uruk; therefore, he called himself "King of all nations."
The devastation of cities and the looting of temples were always condemned and never forgotten by history. Among the rules of war in prehistory was the one saying that the longer the city resisted, the worse fate it met when it was finally captured. If the inhabitants gave up quickly, they could count on the forgiveness of the conqueror, but if the siege lasted a long time because of the citizens' resistance, such a city was doomed. It happened to Girsu and Lagash.
With Sumer secured, Lugalzagesi focused on the Semitic-speaking lands to the north along the Tigris and Euphrates rivers. However, shortly after his Euphrates and Tigris campaigns, Lugalzagesi had little time to secure his power across these vast regions he had just conquered.
"After some two decades of military successes and triumphs, he was brought in a neck stock to the gate of Nippur to be reviled and spat upon by all who passed by.
His conqueror was a Semite named Sargon," the founder of a five-generation Akkadian dynasty that created a capital city at Akkad.
Updated on June 21, 2022
Written by – A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com Senior Staff Writer
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
Expand for referencesReferences:
- Kriwaczek, Paul. Babylon: Mesopotamia and the Birth of Civilization
- N. Kramer, The Sumerians
Arjomand Saïd Amir, Revolution: Structure and Meaning in World History
More From Ancient Pages
-
 Hunter-Gatherer Metallurgy In The Early Iron Age Of Northern Fennoscandia Was Integrated And Advanced
Archaeology | Aug 15, 2023
Hunter-Gatherer Metallurgy In The Early Iron Age Of Northern Fennoscandia Was Integrated And Advanced
Archaeology | Aug 15, 2023 -
 Long-Lost Shipwreck Koning Willem de Tweede Filled With Treasures Discovered By Marine Archaeologists
Underwater Discoveries | May 13, 2025
Long-Lost Shipwreck Koning Willem de Tweede Filled With Treasures Discovered By Marine Archaeologists
Underwater Discoveries | May 13, 2025 -
 Castor And Pollux: Dioscuri Brothers Immortalized In The Night Sky In Greek Beliefs
Featured Stories | Jan 24, 2024
Castor And Pollux: Dioscuri Brothers Immortalized In The Night Sky In Greek Beliefs
Featured Stories | Jan 24, 2024 -
 Bronze Age ‘Washingborough Boat’ Will Reveal Boat Building Techniques Of Ancient People
Archaeology | May 11, 2017
Bronze Age ‘Washingborough Boat’ Will Reveal Boat Building Techniques Of Ancient People
Archaeology | May 11, 2017 -
 Prehistoric Sime Skeleton And Now 15,000-Year-Old Bone Pendant Depicting ‘Venus’ Found In Vlakno Cave, Croatia
Archaeology | Dec 4, 2017
Prehistoric Sime Skeleton And Now 15,000-Year-Old Bone Pendant Depicting ‘Venus’ Found In Vlakno Cave, Croatia
Archaeology | Dec 4, 2017 -
 Non-Invasive Radar Will Search King Tutankhamun’s Tomb For Nefertiti’s Hidden Crypt
Civilizations | Sep 24, 2015
Non-Invasive Radar Will Search King Tutankhamun’s Tomb For Nefertiti’s Hidden Crypt
Civilizations | Sep 24, 2015 -
 Amazing World’s Largest Mosaic Piece Made By 13 Different Ancient Civilizations At Museum Hotel Antakya
Featured Stories | May 9, 2019
Amazing World’s Largest Mosaic Piece Made By 13 Different Ancient Civilizations At Museum Hotel Antakya
Featured Stories | May 9, 2019 -
 Copper Artifacts Reveal Changing Connections In Prehistoric Europe
Archaeology | May 11, 2023
Copper Artifacts Reveal Changing Connections In Prehistoric Europe
Archaeology | May 11, 2023 -
 Levänluhta People Could Survive Fimbulwinter Thanks To Their Diverse Livelihoods
Archaeology | Apr 24, 2020
Levänluhta People Could Survive Fimbulwinter Thanks To Their Diverse Livelihoods
Archaeology | Apr 24, 2020 -
 Arrow Pre-Dating The Vikings Discovered After Being Lost In The Ice For 1,500 Years
Archaeology | Aug 25, 2022
Arrow Pre-Dating The Vikings Discovered After Being Lost In The Ice For 1,500 Years
Archaeology | Aug 25, 2022 -
 Paleolithic Inhabitants Of Cyprus Established Settlements Much Earlier Than Previously Estimated
Archaeology | May 17, 2024
Paleolithic Inhabitants Of Cyprus Established Settlements Much Earlier Than Previously Estimated
Archaeology | May 17, 2024 -
 Unusual Mini Temples Discovered In Ancient Roman Camp In Haltern, Germany
Archaeology | Nov 16, 2023
Unusual Mini Temples Discovered In Ancient Roman Camp In Haltern, Germany
Archaeology | Nov 16, 2023 -
 Homo Longi: Extinct Human Species That May Replace Neanderthals As Our Closest Relatives
Evolution | Sep 14, 2023
Homo Longi: Extinct Human Species That May Replace Neanderthals As Our Closest Relatives
Evolution | Sep 14, 2023 -
 On This Day In History: Julius Caesar Dedicated Temple To Venus Genetrix – On Sep 26, 46 BC
News | Sep 26, 2016
On This Day In History: Julius Caesar Dedicated Temple To Venus Genetrix – On Sep 26, 46 BC
News | Sep 26, 2016 -
 Gordian Knot And How Alexander The Great Managed To Outmaneuver The Problem
Featured Stories | Jul 19, 2024
Gordian Knot And How Alexander The Great Managed To Outmaneuver The Problem
Featured Stories | Jul 19, 2024 -
 El Gigante Offers Lessons In Sustainability, Evolution And Human Adaptation, Courtesy Of The Holocene
Archaeology | Jun 29, 2023
El Gigante Offers Lessons In Sustainability, Evolution And Human Adaptation, Courtesy Of The Holocene
Archaeology | Jun 29, 2023 -
 Walls Of Uruk Built By Sumerian King Gilgamesh 4,500 Years Ago
Featured Stories | Nov 28, 2015
Walls Of Uruk Built By Sumerian King Gilgamesh 4,500 Years Ago
Featured Stories | Nov 28, 2015 -
 Why Napoleon’s Invasion Of Russia Was A Fiasco
Ancient History Facts | Mar 31, 2017
Why Napoleon’s Invasion Of Russia Was A Fiasco
Ancient History Facts | Mar 31, 2017 -
 Stele Of Tell al-Rimah And Deeds Of Assyrian King Adad-nirari Against Rebellious Kings
Featured Stories | Feb 22, 2022
Stele Of Tell al-Rimah And Deeds Of Assyrian King Adad-nirari Against Rebellious Kings
Featured Stories | Feb 22, 2022 -
 Georgia Guidestones Damaged By An Explosive Device – By Whom And Why?
News | Jul 7, 2022
Georgia Guidestones Damaged By An Explosive Device – By Whom And Why?
News | Jul 7, 2022