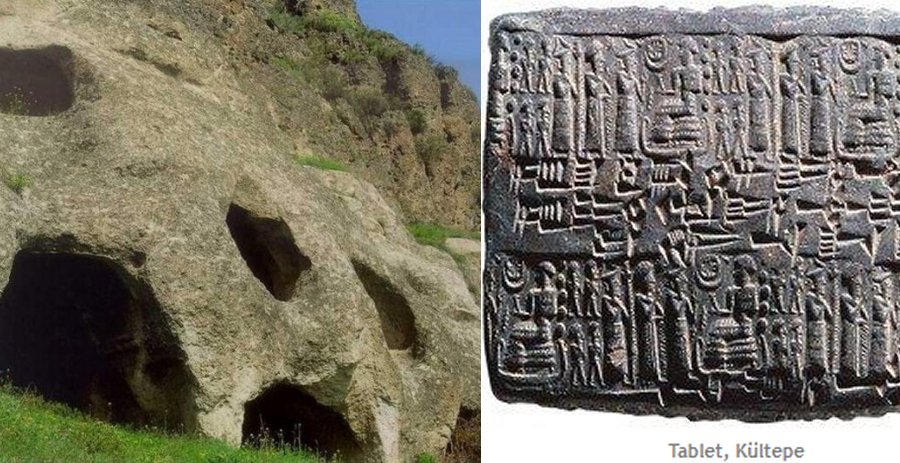
Kültepe: Once Part Of The Kingdom Of Hittites And The Center of a complex network of Assyrian trade colonies in the 2nd millennium B.C.
A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com - Mysterious Kültepe was once part of the kingdom of the Hittites. Excavations revealed ancient artifacts, clay tablets, and intriguing prehistoric structures. Kültepe still has much to reveal.
Kültepe, in Turkish means “Ash Hill,” is an archaeological site located in the Kayseri Province. In the past, it was the capital of the ancient Kingdom of Kanesh and the center of a complex network of Assyrian trade colonies in the 2nd millennium B.C.
The place became a key center of culture and commerce between Anatolia, Syria, and Mesopotamia by the end of the 3rd millennium B.C. and especially during the first quarter of the 2nd millennium B.C.
Over 20,000 Clay Tablets From Cappadocia Discovered
In 1948, archaeologists started to excavate the site and they discovered tens of thousands of archaeological and textual finds.
According to UNESCO, Kültepe is not only a site of utmost importance for Anatolian archaeology, but also for world archaeology. The private archives of the Karum residents have yielded 23,500 clay tablets and envelopes to date.
These are the earliest written documents that illustrated ancient Anatolian history. Life, society, and economy at this site, even the family affairs and personal relationships of its inhabitants, were recorded on clay tablets in the Old Assyrian dialect of the Akkadian language using the cuneiform (wedge-shaped) script, the knowledge of which came into Anatolia with Assyrian merchants.
Unlike royal or temple archives discovered in other ancient centers, the cuneiform archives of Kültepe-Kanesh represent the single largest body of private texts in the ancient Near East. They were kept in archive rooms, neatly arranged inside clay vessels, wooden chests, wicker baskets, or sacks.
Ancient City Of Kültepe Was Destroyed By Fire
The fire which eventually destroyed the city must have started suddenly; as the excavations revealed many documents were still in their envelopes before the merchants could dispatch their recently written letters or open those newly received. The inhabitants left most of their possessions behind to be found by modern archaeologists.
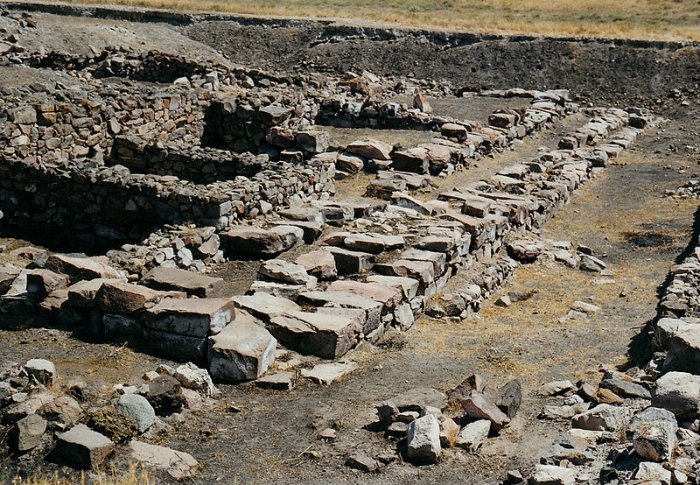
Kültepe - historically very important site - has been successfully excavated since 1948 and still, new excavation works are organized on the Kültepe Kaniş/Karum mound that can shed light on ancient and the very early stages of trade in the region. At present most works focus on the Hittite palace at Kültepe and its surroundings.
The main goal for researchers is to investigate the first eras when the trade started 6,000-7,000 years ago in Kültepe.
The trade hub in this region was crucial for Anatolia for the Middle East as well. In the meantime, the works concentrate on the area dated to 4,500 years ago with the remains of a furnace from 4,500 years ago and also some pieces of an idol made of marble and known as the Kültepe Idol.
Several such idols were unearthed inside the sanctuaries in the palace and in neighboring places inhabited by upper-class people and also lower-class people.
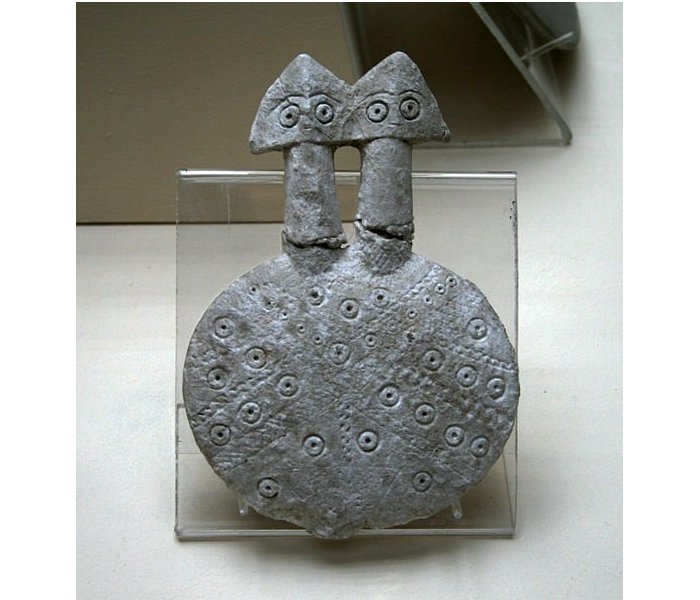

Kültepe Idol. A two-headed mother goddess figurine from Kültepe, an archaeological site in Turkey. This figurine is part of a larger group of flat marble goddess figurines found in Kültepe. Artifact located at the Museum of Anatolian Civilizations, Turkey. Image credit: Noumenon.
The region of Kültepe is a very old place with a history going back millennia and many archaeological findings attest to this history.
The place was inhabited continuously from the Chalcolithic to Roman times, and flourished as an important Hattic center, Hittite and Hurrian city, containing a large merchant colony dated to the Old Assyrian Empire from ca. 21st to 18th centuries BC.
It is a very old place. Today, Kültepe is an archaeological site, about 20 km southwest from the center of Kayseri. Once, it was the capital of the ancient Kingdom of Kanesh, a residental area of indigenous people, and its market place Karum was established in 1950-1650 B.C. by Assyrian colonies. A part of Karum was inhabited by both foreign and native traders who conducted their business.
Kültepe's geographical location contributed much to the place's flourishing period by the end of 3,000 BC to the first quarter of 2,000 BC. Kültepe's culture, politics, and trade thrived between Anatolia, Syria, and Mesopotamia. Today’s Kültepe was established by Hittites in 2000 BC.
Thousands of clay tablets mention seventeen local city-kings who rose up against the famous Naram-Sin of Akkad (ruled c.2254-2218 BC).
It is the site of the discovery of the earliest traces of the Hittite language, and the earliest attestation of any Indo-European language, dated to the 20th century BC. Other tablets mention the conquest of the city of Assur by the kings of Eshnunna, the fall of Assur, and Hammurabi of Babylon.
Written by – A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com Senior Staff Writer
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
Expand for referencesMore From Ancient Pages
-
 Tullus Hostilius: Warrior King Of Rome, Who Succeeded Numa Pompilius And Feared Prophecies
Featured Stories | Mar 6, 2019
Tullus Hostilius: Warrior King Of Rome, Who Succeeded Numa Pompilius And Feared Prophecies
Featured Stories | Mar 6, 2019 -
 Cacao Was Cultivated By Cultures Along The Pacific Coast Around 5,000 Years Ago – New Study
Archaeology | Mar 7, 2024
Cacao Was Cultivated By Cultures Along The Pacific Coast Around 5,000 Years Ago – New Study
Archaeology | Mar 7, 2024 -
 Ancient Treasure Hidden In Perplexing Secret Underground Labyrinth In France – Discovery And Forbidden Excavations – Part 2
Featured Stories | Jan 19, 2020
Ancient Treasure Hidden In Perplexing Secret Underground Labyrinth In France – Discovery And Forbidden Excavations – Part 2
Featured Stories | Jan 19, 2020 -
 2,000-Year-Old Medusa Mosaic Is Considered The Pearl Of Ancient City Of Kibyra
Archaeology | Aug 25, 2020
2,000-Year-Old Medusa Mosaic Is Considered The Pearl Of Ancient City Of Kibyra
Archaeology | Aug 25, 2020 -
 Story Behind A Huge Mysterious Ancient Rock Art Site In Central Queensland Revealed By Scientists
Archaeology | Sep 21, 2022
Story Behind A Huge Mysterious Ancient Rock Art Site In Central Queensland Revealed By Scientists
Archaeology | Sep 21, 2022 -
 On This Day In History: The Battle Of Fulford Was Fought – On Sep 20, 1066 AD
News | Sep 20, 2015
On This Day In History: The Battle Of Fulford Was Fought – On Sep 20, 1066 AD
News | Sep 20, 2015 -
 On This Day In History: Berlin Opened For One Day – On Dec 20, 1963
News | Dec 20, 2016
On This Day In History: Berlin Opened For One Day – On Dec 20, 1963
News | Dec 20, 2016 -
 13,000-Year-Old Engraving May Depict First Paleolithic Social Group Of Humans
Archaeology | Dec 4, 2015
13,000-Year-Old Engraving May Depict First Paleolithic Social Group Of Humans
Archaeology | Dec 4, 2015 -
 Secret Dwelling Place Of Reptilian And Dragon-Like Creatures In Europe
Featured Stories | Jul 18, 2018
Secret Dwelling Place Of Reptilian And Dragon-Like Creatures In Europe
Featured Stories | Jul 18, 2018 -
 Gigantic Horizontally Lying Stones Of Ancient City Of Baalbek
Civilizations | Mar 10, 2017
Gigantic Horizontally Lying Stones Of Ancient City Of Baalbek
Civilizations | Mar 10, 2017 -
 Was Alulim, First King Of Sumer And Eridu Biblical Adam?
Biblical Mysteries | Mar 14, 2019
Was Alulim, First King Of Sumer And Eridu Biblical Adam?
Biblical Mysteries | Mar 14, 2019 -
 The Ebers Papyrus – Most Famous Plant Medicine ‘Encyclopedia’ Of Ancient Egypt
Civilizations | Feb 3, 2016
The Ebers Papyrus – Most Famous Plant Medicine ‘Encyclopedia’ Of Ancient Egypt
Civilizations | Feb 3, 2016 -
 Bora People Of The Northwest Amazon Use Drums To Speak Over Large Distances
Archaeology | May 4, 2018
Bora People Of The Northwest Amazon Use Drums To Speak Over Large Distances
Archaeology | May 4, 2018 -
 Stone Tools Reflect Three Waves Of Migration Of The Earliest Homo Sapiens Into Europe
Archaeology | May 4, 2023
Stone Tools Reflect Three Waves Of Migration Of The Earliest Homo Sapiens Into Europe
Archaeology | May 4, 2023 -
 Did Ancient Civilizations Possess Knowledge Of Time Travel?
Ancient Technology | Sep 17, 2018
Did Ancient Civilizations Possess Knowledge Of Time Travel?
Ancient Technology | Sep 17, 2018 -
 Hephaestus (Hephaistos) – God Of Fire And Master Craftsman Constructed Talos, First Greek Robot And Divine Weapons Of The Gods
Featured Stories | Jul 7, 2018
Hephaestus (Hephaistos) – God Of Fire And Master Craftsman Constructed Talos, First Greek Robot And Divine Weapons Of The Gods
Featured Stories | Jul 7, 2018 -
 Large Fortress And Wall Uncovered On The Nile Delta Mark Power Of Egypt’s Canal Of the Pharaohs
Archaeology | Dec 29, 2017
Large Fortress And Wall Uncovered On The Nile Delta Mark Power Of Egypt’s Canal Of the Pharaohs
Archaeology | Dec 29, 2017 -
 Deception And Hidden Truth – Ancient Struggle Of The Eagle And Serpent – Part 1
Ancient Symbols | Sep 4, 2019
Deception And Hidden Truth – Ancient Struggle Of The Eagle And Serpent – Part 1
Ancient Symbols | Sep 4, 2019 -
 183-Million-Year-Old Fossils: Jurassic Marine World In A Farmer’s Field
Fossils | Jul 31, 2022
183-Million-Year-Old Fossils: Jurassic Marine World In A Farmer’s Field
Fossils | Jul 31, 2022 -
 Underwater Excavations: Greek And Danish Archaeologists Research Ancient Harbor Town Lechaion
Archaeology | Dec 25, 2015
Underwater Excavations: Greek And Danish Archaeologists Research Ancient Harbor Town Lechaion
Archaeology | Dec 25, 2015