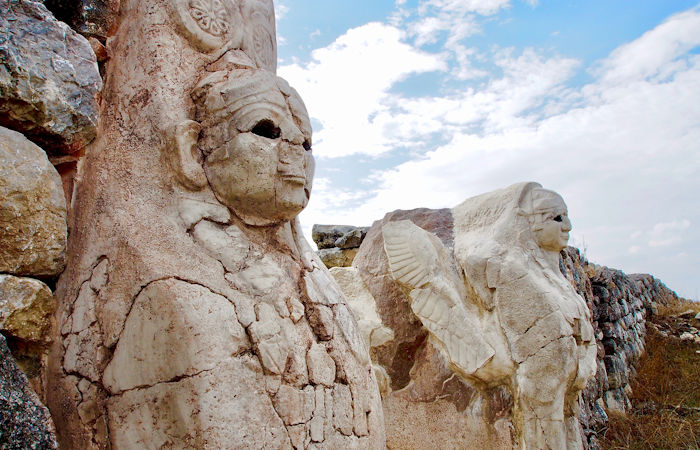
Magnificent Hattusa: Capital Of The Hittite Empire
A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com - Hattusa was the capital of the kingdom of the Hittites in the late Bronze Age. In the 2nd millennium BC, the kingdom stretched from the Aegean across Anatolia, Turkey, northern Syria, and to the Euphrates River.
In ancient times, it was a great city, and even today, its magnificent ruins attest to the greatness of this place. The population of the old capital is estimated to have been 50,000 at its most.
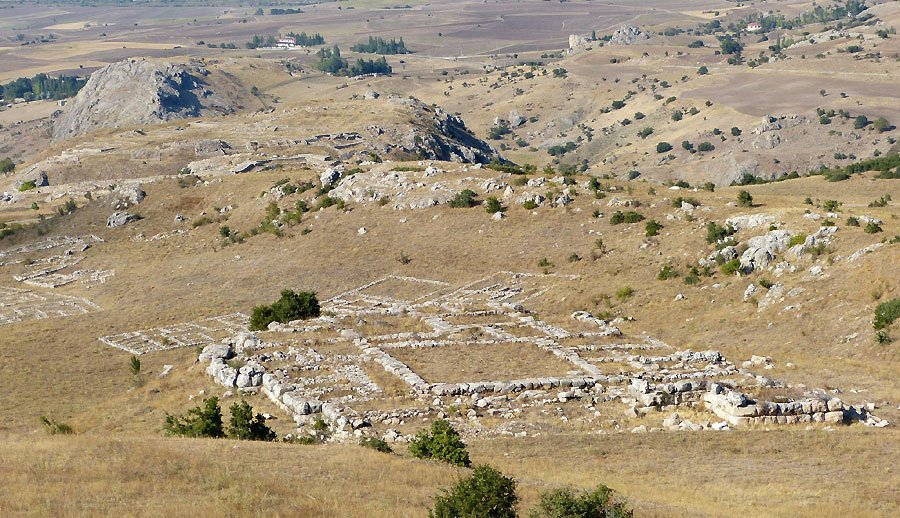 Hattusa is one of Turkey’s great ruins of the capital of the Hittite Empire.
Hattusa is one of Turkey’s great ruins of the capital of the Hittite Empire.
Hattusa has a rich history with its six-kilometre walls surrounding the ancient city, its monumental gates, the 71-meter-long underground passage, and 31 temples unearthed so far. The Lion Gate, the King Gate, and the Yazılıkaya Open Air Temple are some of the impressive landmarks.
The first settling around Hattusa took place in the 6th millennium BC during the Chalcolithic period, when small, widely scattered hamlets appeared, most particularly on mountain slopes and rocky outcroppings. Late in the 3rd millennium BC, towards the end of the Early Bronze Age, a Hattian settlement developed, marking the beginning of continuous occupation at the site.
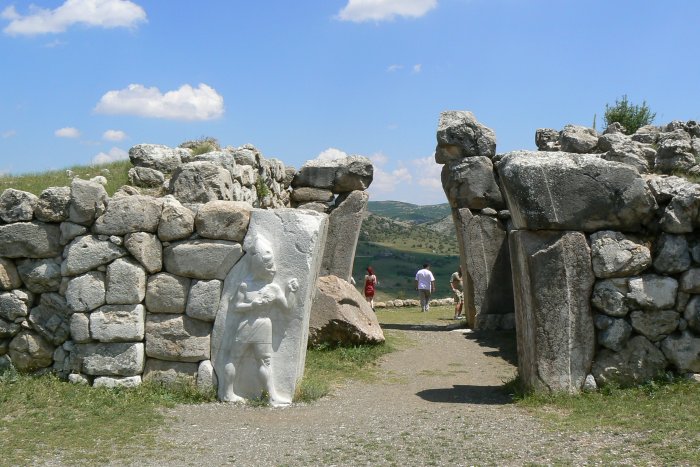 Hattusha - The King Gate Image credit: Wikipedia
Hattusha - The King Gate Image credit: Wikipedia
The Hittites ruled the central Anatolian kingdom of Hatti from c. 1900 - to 800 BCE. They formed the earliest known Anatolian civilization and employed an advanced system of government based on an established legal system. Their military force was well trained, well equipped, and employed chariots that were the lightest and fastest of their time.
Hattusa consists of two sites: the Lower City and the Upper City. The Hittites built their capital on a site that could be well defended.
The ruins of the upper city’s fortification reveal that the city was surrounded by a double wall (forming a perimeter of roughly 8 km) with more than a hundred towers and, as far as is known today, five gateways: two in the west, Lion’s Gate in the south-west, the King’s Gate in the south-east and a procession gate, the Sphinx Gate in the south of the city.
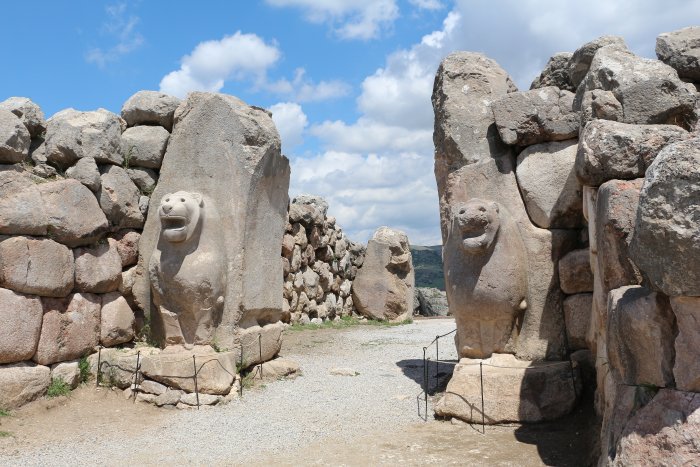 Hattusa - The Lion Gate in the south-west. Image credit: Bernard Gagnon - CC BY-SA 2.5
Hattusa - The Lion Gate in the south-west. Image credit: Bernard Gagnon - CC BY-SA 2.5
To the north, beyond the walls, there was a necropolis cut into the rock at Osmankayasi and the great sanctuary of Yazilikaya, whose walls decorated with bas-reliefs are the undisputed masterpiece of Hittite art.
Hattusa - The Sphinx Gate. Adobe Stock - marista
The best-preserved ruin of a Hittite Temple from the 13th century B.C., known as the Great Temple, is located in the Lower City. The Great Temple was dedicated to the god of storms and the goddess of the Sun, Arinna, and surrounded by an array of buildings, including stores.
Thousands of cuneiform tablets were found in this area. One of the most important discoveries has been the cuneiform royal archives of clay tablets, consisting of official correspondence and contracts, legal codes, procedures for cult ceremonies, oracular prophecies, and literature of the ancient Near East.
One particularly important tablet, currently on display at the Istanbul Archaeology Museum, details the terms of a peace settlement reached years after the Battle of Kadesh between the Hittites and the Egyptians under Ramesses II in 1259 or 1258 BC.
Twelve Hittite gods of the Underworld in the nearby Yazılıkaya, a sanctuary of Hattusa. Image credit: WikipediaOther temples of similar date and shape, albeit generally smaller, are situated in the Upper City, which mostly consisted of a temple city for the gods and goddesses of the Hittite and Hurrian pantheon. The remains of a densely inhabited city district were unearthed in the Lower City, where their foundations and arrangement can still be seen in the area north of the Great Temple.
The site, discovered in 1834, was not comprehensively excavated until 1906. The site has been on the World Heritage List since 1986.
Written by – A. Sutherland AncientPages.com Staff Writer
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
Expand for referencesMore From Ancient Pages
-
 Skeleton Of An Ancient Roman Mercenary Buried With His Sword Discovered In South Wales
Archaeology | Apr 6, 2022
Skeleton Of An Ancient Roman Mercenary Buried With His Sword Discovered In South Wales
Archaeology | Apr 6, 2022 -
 Different Story Of Odin’s Sons Balder And Hoder In Norse Mythology
Featured Stories | Nov 26, 2020
Different Story Of Odin’s Sons Balder And Hoder In Norse Mythology
Featured Stories | Nov 26, 2020 -
 What Is The Codex Mendoza?
Ancient History Facts | Feb 14, 2016
What Is The Codex Mendoza?
Ancient History Facts | Feb 14, 2016 -
 Scribes: One Of The Noblest And Highly Recommended Professions In Ancient Egypt
Featured Stories | May 10, 2023
Scribes: One Of The Noblest And Highly Recommended Professions In Ancient Egypt
Featured Stories | May 10, 2023 -
 Mysterious Sumerian Star Tablet And Strange Divine Omens – Sacred Knowledge Of The Gods – Part 1
Ancient Mysteries | Feb 14, 2021
Mysterious Sumerian Star Tablet And Strange Divine Omens – Sacred Knowledge Of The Gods – Part 1
Ancient Mysteries | Feb 14, 2021 -
 Disgusting Vandalism And Looting Of Viking Graves In Norway
News | Nov 6, 2020
Disgusting Vandalism And Looting Of Viking Graves In Norway
News | Nov 6, 2020 -
 Mysterious Megaliths Of Russia May Offer Evidence Of An Ancient Advanced Lost Civilization
Ancient Technology | Jul 22, 2017
Mysterious Megaliths Of Russia May Offer Evidence Of An Ancient Advanced Lost Civilization
Ancient Technology | Jul 22, 2017 -
 Rare Stone Age Artifacts Found In Norway Offer Evidence Of Migration From The East
Archaeology | Aug 24, 2023
Rare Stone Age Artifacts Found In Norway Offer Evidence Of Migration From The East
Archaeology | Aug 24, 2023 -
 Extremely Rare Ancient Coin Of Short-Lived Roman Ruler Laelianus Discovered
Archaeology | Jun 25, 2019
Extremely Rare Ancient Coin Of Short-Lived Roman Ruler Laelianus Discovered
Archaeology | Jun 25, 2019 -
 7.2-Million-Year-Old Pre-Human Remains Suggest Our First Ancestor Came From Europe Not Africa
Archaeology | May 23, 2017
7.2-Million-Year-Old Pre-Human Remains Suggest Our First Ancestor Came From Europe Not Africa
Archaeology | May 23, 2017 -
 7,000-Year-Old Ibex Remains Found Under The Ice In Italy Are 1,700 Years Older Than Ötzi!
Archaeology | Dec 14, 2022
7,000-Year-Old Ibex Remains Found Under The Ice In Italy Are 1,700 Years Older Than Ötzi!
Archaeology | Dec 14, 2022 -
 Before The Pharaohs: The Evidence For Advanced Civilization In Egypt’s Mysterious Prehistory
Civilizations | Apr 14, 2017
Before The Pharaohs: The Evidence For Advanced Civilization In Egypt’s Mysterious Prehistory
Civilizations | Apr 14, 2017 -
 Were The Knights Templar Guilty Or Innocent Of The Crimes Laid Against Them?
Featured Stories | Oct 9, 2025
Were The Knights Templar Guilty Or Innocent Of The Crimes Laid Against Them?
Featured Stories | Oct 9, 2025 -
 The Apaches’ Mysterious Encounter With Unknown Beings
Featured Stories | Jun 10, 2024
The Apaches’ Mysterious Encounter With Unknown Beings
Featured Stories | Jun 10, 2024 -
 Does Palenque Mask Depict Mayan Ruler Pakal? New Discovery At Palenque
Archaeology | Aug 27, 2018
Does Palenque Mask Depict Mayan Ruler Pakal? New Discovery At Palenque
Archaeology | Aug 27, 2018 -
 Inscription On Rare Tetrarchic Boundary Stone Found At Biblical Site Of Abel Beth Maacah, Israel Has Been Deciphered
Archaeology | Jan 21, 2025
Inscription On Rare Tetrarchic Boundary Stone Found At Biblical Site Of Abel Beth Maacah, Israel Has Been Deciphered
Archaeology | Jan 21, 2025 -
 Abric Romaní Cave: New evidence indicates Neanderthals used to heat water some 60,000 years ago
Human Beginnings | Aug 31, 2015
Abric Romaní Cave: New evidence indicates Neanderthals used to heat water some 60,000 years ago
Human Beginnings | Aug 31, 2015 -
 Ancient DNA Reconstructs Rise Of Largest Empires In History Of Inner Asia
Archaeology | Nov 6, 2020
Ancient DNA Reconstructs Rise Of Largest Empires In History Of Inner Asia
Archaeology | Nov 6, 2020 -
 Ancient Papyrus Reveals Millennia Old Astronomical Secret: The ‘Demon Star’ Algol Does Exist
Civilizations | Aug 23, 2015
Ancient Papyrus Reveals Millennia Old Astronomical Secret: The ‘Demon Star’ Algol Does Exist
Civilizations | Aug 23, 2015 -
 “Touchstones” For Social Belonging: How Did Ancient Pastoralists In South Arabia Adapt To Climate Change?
Archaeology | Jun 2, 2025
“Touchstones” For Social Belonging: How Did Ancient Pastoralists In South Arabia Adapt To Climate Change?
Archaeology | Jun 2, 2025

