Why Is Rome Called ‘The Eternal City’?
Conny Waters - AncientPages.com - Have you ever wondered why Rome became known as the "Eternal City? The city's nickname can be traced to an ancient myth, ancient historical writings, and the old Romans' beliefs in the greatness of their city.
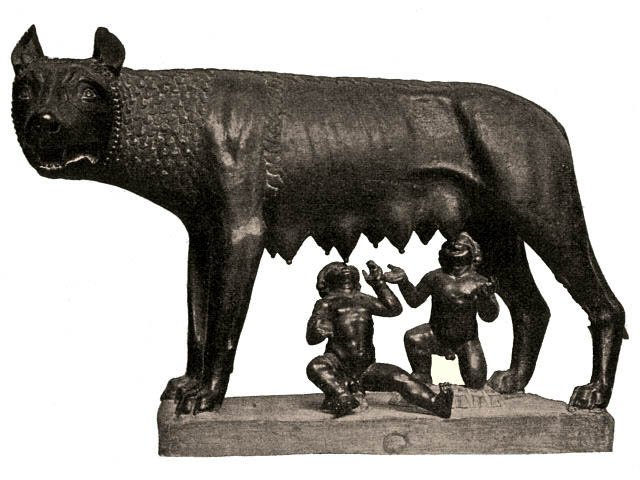
The Capitoline she-wolf with the boys Romulus and Remus. Museo Nuovo in the Palazzo dei Conservatori, Rome. Rome is much older than the myth about Romulus and Remus. Benutzer:Wolpertinger - Public Domain
According to an ancient legend, the city of Rome was founded on April 21, 753 B.C. by Romulus.
Romulus and Remus were twin brothers and sons of the god Mars. Thrown into the river Tiber by a wicked uncle hoping they would drown, the small boys were rescued by a wolf who fed them.
When Romulus and Remus became adults, they decided to establish their city, and each set out to find the best location. They were later discovered and cared for by a shepherd and his wife: Faustulus and Acca Larentia. One day, the two brothers quarreled over where the site should be, and his brother killed Remus.
It left Romulus the sole founder of the new city, and he gave his name to it – Rome. Now, this is just a myth, and the history of Rome goes much further back in time.
According to the legend, Romulus became the first king of Rome in 753 BC. Legends say Numa Pompilius was the second king of Rome, but he was not a warrior king but a statesman and politician.
Nevertheless, archaeologists have discovered artifacts that prove Rome was inhabited much earlier than 753 B.C.
Rome was known as the "Eternal City" because civilizations had lived there for thousands of years. The ancient Roman Empire was mighty, and it had many enemies. Yet, ancient Romans managed to defeat the Carthaginians and Etruscans and extended their empire throughout Europe and Africa. No one underestimated the greatness of the ancient Roman Empire.
Between c. 100 B.C to around 400 A.D, the city of Rome was the largest in the world.
Around 500 A.D., Empire's populace grew to an estimated 50 to 90 million. At the time, this was roughly 20% of the world's population.
Roman writers and poets boasted about their city's greatness. In his epic poem The Aeneid, the poet Virgil wrote the line imperium sine fine – an empire without end.
The first explicit reference to Rome as the Eternal City occurred in the 1st century B.C. Poet Albius Tibullus (55 BC - 19 BC) wrote ‘Romulus aeternae nondum formaverat urbis moenia, consorti non habitanda Remo’ – Tibullus, from Elegies.
In other words, 'not yet had Romulus drawn up the Eternal City's walls, where Remus as co-ruler was fated not to live.
Ancient writers such as Ovid and Livy also took up the expression.
It's no wonder that ancient Romans thought that whatever happened to the rest of the world, Rome would last forever. Rome became known as the "Eternal City."
Rome is called the "Caput Mundi" (Capital of the World). Although the ancient Roman Empire is long gone, we still call it the "Eternal City."
Romulus and Remus were twin brothers and sons of the god Mars. A wicked uncle threw them into the river Tiber, hoping they would drown, but a wolf who fed them rescued them.
They were later discovered and cared for by a shepherd and his wife: Faustulus and Acca Larentia. When Romulus and Remus became adults, they decided to establish their own city, and each set out to find the best location. One day, the two brothers quarreled over where the site should be, and his brother killed Remus.
This left Romulus the sole founder of the new city, and he gave his name to it – Rome. Now, this is just a myth, and the history of Rome goes much further back in time.
According to the legend, Romulus became the first king of Rome in 753 BC. Legends say Numa Pompilius was the second king of Rome, but he was not a warrior king but rather a statesman and politician.
Nevertheless, archaeologists have discovered artifacts showing that Rome was inhabited much earlier than 753 B.C.
Rome was known as the “Eternal City” because civilizations had lived there for thousands of years. The ancient Roman Empire was very powerful and had many enemies. Yet, the ancient Romans managed to defeat the Carthaginians and Etruscans and extend their empire throughout Europe and Africa. No one underestimated the greatness of the ancient Roman Empire.
Between 100 B.C. to around 400 A.D., Rome was the largest city in the world. Around 500 A.D., the Empire's populace grew to an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants. At the time, this was roughly 20% of the world's population.
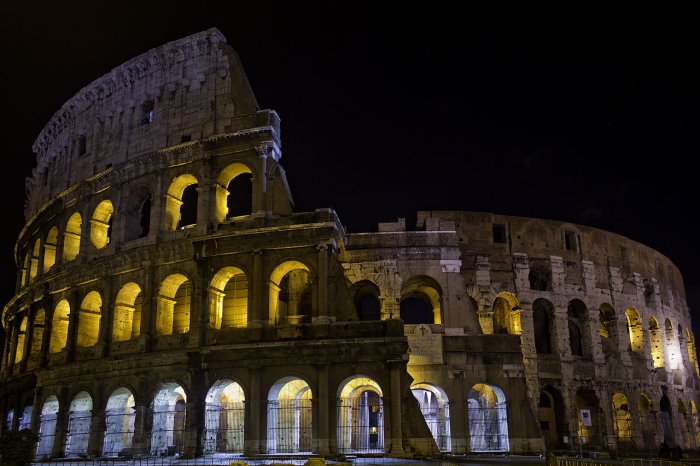
Colosseum at night. Image credit: Ramesh - CC BY-SA 3.0
Roman writers and poets boasted about their city’s greatness. In his epic poem The Aeneid, the poet Virgil wrote the line imperium sine fine – an empire without end.
The first explicit reference to Rome as the Eternal City occurred in the 1st century B.C. Poet Albius Tibullus (55 BC - 19 BC) wrote ‘Romulus aeternae nondum formaverat urbis moenia, consorti non habitanda Remo’ – Tibullus, from Elegies.
In other words, ‘not yet had Romulus drawn up the Eternal City’s walls, where Remus as co-ruler was fated not to live.’
The expression was also taken up by ancient writers such as Ovid and Livy.
It’s no wonder that ancient Romans thought that whatever happened to the rest of the world, Rome would last forever. Rome became known as the “Eternal City”.
Rome is also called the "Caput Mundi" (Capital of the World). The ancient Roman Empire is long gone, but we still call Rome the “Eternal City.”
First version of this article was published on Ancient Pages on April 4, 2018
Written by Conny Waters – AncientPages.com Staff Writer
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
More From Ancient Pages
-
 Limestone Stela Of Liberation Discovered In Kom Ombo Temple In Aswan, Egypt
Archaeology | Oct 17, 2018
Limestone Stela Of Liberation Discovered In Kom Ombo Temple In Aswan, Egypt
Archaeology | Oct 17, 2018 -
 Magnificent Reconstruction Of Scotland’s Largest Pictish Fort Burghead
Archaeology | Nov 3, 2021
Magnificent Reconstruction Of Scotland’s Largest Pictish Fort Burghead
Archaeology | Nov 3, 2021 -
 ‘Little Caesar’: Forgotten ‘King Of Kings’ Who Died Very Young
Featured Stories | May 11, 2020
‘Little Caesar’: Forgotten ‘King Of Kings’ Who Died Very Young
Featured Stories | May 11, 2020 -
 Connection Between Viruses And Ancestors Of All Complex Life Has Been Found
Archaeology | Jul 1, 2022
Connection Between Viruses And Ancestors Of All Complex Life Has Been Found
Archaeology | Jul 1, 2022 -
 Ancient Roman Coins Thought To Be Fakes Are Authentic – Experts Say
Archaeology | Nov 23, 2022
Ancient Roman Coins Thought To Be Fakes Are Authentic – Experts Say
Archaeology | Nov 23, 2022 -
 Unexplained Historical Mass Disappearances – Lost Without Trace – Part 1
Featured Stories | May 31, 2019
Unexplained Historical Mass Disappearances – Lost Without Trace – Part 1
Featured Stories | May 31, 2019 -
 Bizarre Ancient Capuchin Crypt ‘Decorated’ With The Bones Of 4,000 Monks
Ancient Traditions And Customs | Nov 22, 2018
Bizarre Ancient Capuchin Crypt ‘Decorated’ With The Bones Of 4,000 Monks
Ancient Traditions And Customs | Nov 22, 2018 -
 Ancient Tomb Of Maya Ruler Te’ Chan Ahk Discovered In Guatemala
News | Sep 14, 2017
Ancient Tomb Of Maya Ruler Te’ Chan Ahk Discovered In Guatemala
News | Sep 14, 2017 -
 Rare Gilded Mask Discovered On Mummy Of Ancient Egyptian Priest Serving Sky Goddess Mut
Archaeology | Jul 17, 2018
Rare Gilded Mask Discovered On Mummy Of Ancient Egyptian Priest Serving Sky Goddess Mut
Archaeology | Jul 17, 2018 -
 Complex Of Goguryeo Tombs: Beautiful Ancient Wall Paintings Displaying History And Mythology Of North Korea
Civilizations | Oct 19, 2018
Complex Of Goguryeo Tombs: Beautiful Ancient Wall Paintings Displaying History And Mythology Of North Korea
Civilizations | Oct 19, 2018 -
 Mystery Of The Proto-Elamite Tablets – Cracking The World’s Oldest Undeciphered Writing
Artifacts | Oct 29, 2012
Mystery Of The Proto-Elamite Tablets – Cracking The World’s Oldest Undeciphered Writing
Artifacts | Oct 29, 2012 -
 Will Star Goddess Astraea Return To Earth With Second Golden Age Or Apocalypse?
Featured Stories | Aug 1, 2020
Will Star Goddess Astraea Return To Earth With Second Golden Age Or Apocalypse?
Featured Stories | Aug 1, 2020 -
 Mysterious Kola Pyramids Built By An Unknown Lost Ancient Civilization Can Rewrite Ancient History
Civilizations | Aug 3, 2020
Mysterious Kola Pyramids Built By An Unknown Lost Ancient Civilization Can Rewrite Ancient History
Civilizations | Aug 3, 2020 -
 2,000-Year-Old Roman Road Discovered In Cluj-Napoca, Romania
Archaeology | Jan 23, 2023
2,000-Year-Old Roman Road Discovered In Cluj-Napoca, Romania
Archaeology | Jan 23, 2023 -
 2,000-Year-Old Historical Tombs Unearthed In Close Vicinity To Ancient City Of Laodicea
Archaeology | Jan 23, 2020
2,000-Year-Old Historical Tombs Unearthed In Close Vicinity To Ancient City Of Laodicea
Archaeology | Jan 23, 2020 -
 Linked Human Skeletons Lying In Spiral Circle Unearthed In Pre-Aztec Burial Pit Near Mexico City
Archaeology | Feb 7, 2018
Linked Human Skeletons Lying In Spiral Circle Unearthed In Pre-Aztec Burial Pit Near Mexico City
Archaeology | Feb 7, 2018 -
 1,400-Year-Old Christian Chalice With Etched Symbols Found In Rubble At Vindolanda Fort, Britain
Artifacts | Sep 1, 2020
1,400-Year-Old Christian Chalice With Etched Symbols Found In Rubble At Vindolanda Fort, Britain
Artifacts | Sep 1, 2020 -
 Ancient Hebrew Inscription Reveals Location Of Biblical Mount Sinai
Archaeology | Nov 21, 2019
Ancient Hebrew Inscription Reveals Location Of Biblical Mount Sinai
Archaeology | Nov 21, 2019 -
 Mystery Of Vangchhia Ancient Site: Water Pavilion And Ingenious Idea Of Water Harvesting
Archaeology | Feb 21, 2019
Mystery Of Vangchhia Ancient Site: Water Pavilion And Ingenious Idea Of Water Harvesting
Archaeology | Feb 21, 2019 -
 Viking Fashion: Men And Women Were Vain And Very Clean During The Viking Age
Ancient History Facts | May 17, 2024
Viking Fashion: Men And Women Were Vain And Very Clean During The Viking Age
Ancient History Facts | May 17, 2024


