Why Did Ancient Egyptians Use Pillows Made Of Stone?
Conny Waters - AncientPages.com - It might sound odd, but the ancient Egyptians did, in fact, use pillows made of stone. The first people to use pillows lived in the early civilizations of Mesopotamia around 7,000 BC. In those days, only rich people could afford to use pillows.
The number of pillows symbolized status, so the more pillows one owned, the more influence one held.
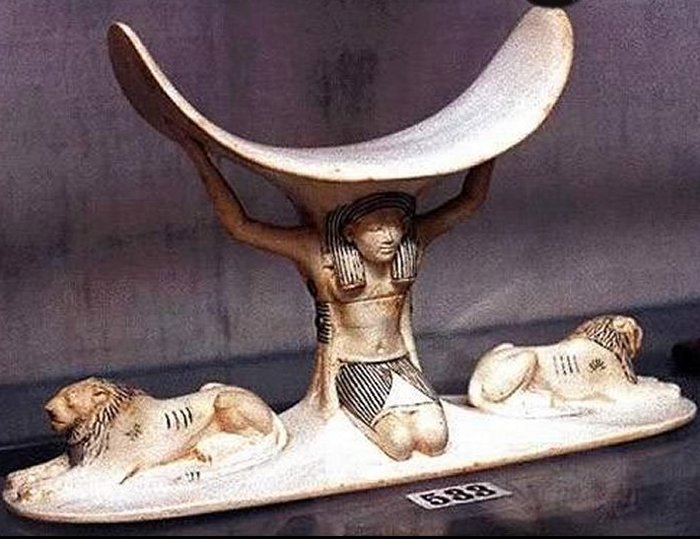

The headrest of Shu ( “He Who Rises Up”), the Egyptian God of Air, atmosphere, and dry winds. Cairo Museum
In ancient Egypt, pillows were associated with mummies and tombs. Based on archaeological findings, it has been established that the ancient Egyptian pillows date back to 2055-1985 B.C.
Pillows in Mesopotamia were formed from stone in the shape of a crescent. This idea was born to support the neck. The pillow had the function of keeping the head in such a position as to protect against worms. It is necessary to add that these people slept on the ground, and the correct position of the head prevented insects from getting into the nose, ears, and eyes. The pillow created in this way, although not comfortable for us, helped to recede the pain in the back, neck, and shoulders.
Ancient Egyptian pillows were made of stone, wood, alabaster, or glass. These pillows were not uncommon and were used because the Egyptians believed the head was an important spiritual and vital center of the body. It was sacred and considered to be the essence of life.
The ancient Egyptian word for a headrest (wrs), related to the word rs, means, "dream” and religious texts often mention stone pillows saying, “sleep well” and emphasize the importance of “raising one’s head higher” while sleeping and even n the afterlife.
As they were hard, stone pillows provided support to a corpse’s head, uphold body vigor, improved blood circulation, and maintained the vitality of the body. They also helped to avoid pain and diseases and, additionally, could keep demons away.
Written by Conny Waters – AncientPages.com Staff Writer
Updated on November 9, 2023
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
Expand for referencesMore From Ancient Pages
-
 200,000-Year-Old Stone Engravings Found In Marbella Could Rewrite The History Of Prehistoric Art
Archaeology | Mar 17, 2025
200,000-Year-Old Stone Engravings Found In Marbella Could Rewrite The History Of Prehistoric Art
Archaeology | Mar 17, 2025 -
 Mythical Egyptian Bennu Bird And Deity
Egyptian Mythology | Jun 5, 2016
Mythical Egyptian Bennu Bird And Deity
Egyptian Mythology | Jun 5, 2016 -
 South Korea’s Silla-Era Tombs Reveal More Priceless Jewelry
Archaeology | Sep 9, 2020
South Korea’s Silla-Era Tombs Reveal More Priceless Jewelry
Archaeology | Sep 9, 2020 -
 Oldest Evidence Of Beer Comes From Raqefet Cave, Dating Back To 11,000 B.C.
Archaeology | Sep 27, 2024
Oldest Evidence Of Beer Comes From Raqefet Cave, Dating Back To 11,000 B.C.
Archaeology | Sep 27, 2024 -
 Why Were Ancient ‘Puppet’ Figurines Placed Atop A Pre-Columbian Pyramid In El Salvador?
Archaeology | Mar 5, 2025
Why Were Ancient ‘Puppet’ Figurines Placed Atop A Pre-Columbian Pyramid In El Salvador?
Archaeology | Mar 5, 2025 -
 Tomb of the 26th dynasty vizier of Upper Egypt discovered in South Assassif, Luxor
Civilizations | Aug 31, 2015
Tomb of the 26th dynasty vizier of Upper Egypt discovered in South Assassif, Luxor
Civilizations | Aug 31, 2015 -
 Ezekiel’s Secret Ancient Knowledge About Lost Worlds – Thought-Provoking Theory Examined
Ancient Mysteries | May 3, 2019
Ezekiel’s Secret Ancient Knowledge About Lost Worlds – Thought-Provoking Theory Examined
Ancient Mysteries | May 3, 2019 -
 Underwater Artifacts Shed New Light On Battle Of The Egadi Islands Between Romans And Carthage
Archaeology | Dec 16, 2020
Underwater Artifacts Shed New Light On Battle Of The Egadi Islands Between Romans And Carthage
Archaeology | Dec 16, 2020 -
 Sami God Horagalles Who Ruled Over Rain, Fire And Thunder Hated Evil Spirits
Featured Stories | Feb 11, 2024
Sami God Horagalles Who Ruled Over Rain, Fire And Thunder Hated Evil Spirits
Featured Stories | Feb 11, 2024 -
 Ancient Viking Age Music Recreated – This Is What It Sounds Like
Featured Stories | Sep 20, 2020
Ancient Viking Age Music Recreated – This Is What It Sounds Like
Featured Stories | Sep 20, 2020 -
 Controversial Theory Suggests Atlantis Was In Scandinavia – Surprising Evidence Presented By Ancient Writer
Ancient Mysteries | Sep 5, 2018
Controversial Theory Suggests Atlantis Was In Scandinavia – Surprising Evidence Presented By Ancient Writer
Ancient Mysteries | Sep 5, 2018 -
 Radiocarbon Dating Of Santorini Eruption And Egyptian Artifacts Shed New Light On Pharaoh Ahmose And The New Kingdom
Archaeology | Oct 23, 2025
Radiocarbon Dating Of Santorini Eruption And Egyptian Artifacts Shed New Light On Pharaoh Ahmose And The New Kingdom
Archaeology | Oct 23, 2025 -
 On This Day In History: Chinese General Koxinga Seizes The Island Of Taiwan – On Feb 1, 1662
News | Feb 1, 2017
On This Day In History: Chinese General Koxinga Seizes The Island Of Taiwan – On Feb 1, 1662
News | Feb 1, 2017 -
 Enigma Of Skull From Petralona Cave In Greece Is Solved And Changes The Human Evolution’s History
Evolution | Aug 21, 2025
Enigma Of Skull From Petralona Cave In Greece Is Solved And Changes The Human Evolution’s History
Evolution | Aug 21, 2025 -
 Magnificent 2,000-Year-Old Marble Head Of God Dionysus Discovered In Rome
Archaeology | Jun 17, 2019
Magnificent 2,000-Year-Old Marble Head Of God Dionysus Discovered In Rome
Archaeology | Jun 17, 2019 -
 Why Is The Battle Of Gaugamela Called Broken ‘Camel’s Back’?
Ancient History Facts | Jul 1, 2020
Why Is The Battle Of Gaugamela Called Broken ‘Camel’s Back’?
Ancient History Facts | Jul 1, 2020 -
 Viklaumadonna Hides A Thousands-Year-Old Secret
Artifacts | Jan 5, 2020
Viklaumadonna Hides A Thousands-Year-Old Secret
Artifacts | Jan 5, 2020 -
 Pharaoh Ay – A Man With A Hidden Agenda Or A Victim Of Unfortunate Circumstances?
Featured Stories | Feb 5, 2019
Pharaoh Ay – A Man With A Hidden Agenda Or A Victim Of Unfortunate Circumstances?
Featured Stories | Feb 5, 2019 -
 Tooth Analysis Sheds Light On South Australia’s Early Colonial History
Archaeology | Jul 6, 2022
Tooth Analysis Sheds Light On South Australia’s Early Colonial History
Archaeology | Jul 6, 2022 -
 3,000-Year-Old Shoe Found On A Beach In Kent, UK
Archaeology | Feb 24, 2023
3,000-Year-Old Shoe Found On A Beach In Kent, UK
Archaeology | Feb 24, 2023
