Parthians: Their Great Empire And Skilled Horse Archers
A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com - The Parthian people established an empire that lasted almost 500 years, from the mid-3rd century BC until 224 CE. Their empire was the most lasting of the empires of the ancient Near East.
They came to power under king Mithradates the Great (171-138 BC); their territories stretched from the Euphrates River in the west to Central Asia and the borders of Bactria in the east. The Parthian empire occupied Iraq, Armenia, all of modern Iran, parts of Turkey, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, Afghanistan and Tajikistan, and for short time, also territories in Pakistan, Syria, Lebanon, Israel and Palestine.
Strangely, despite their enormous role in forming a strong link between the peoples of East Asia and Europe - the Parthians were overshadowed by the Achaemenids and Sassanids.
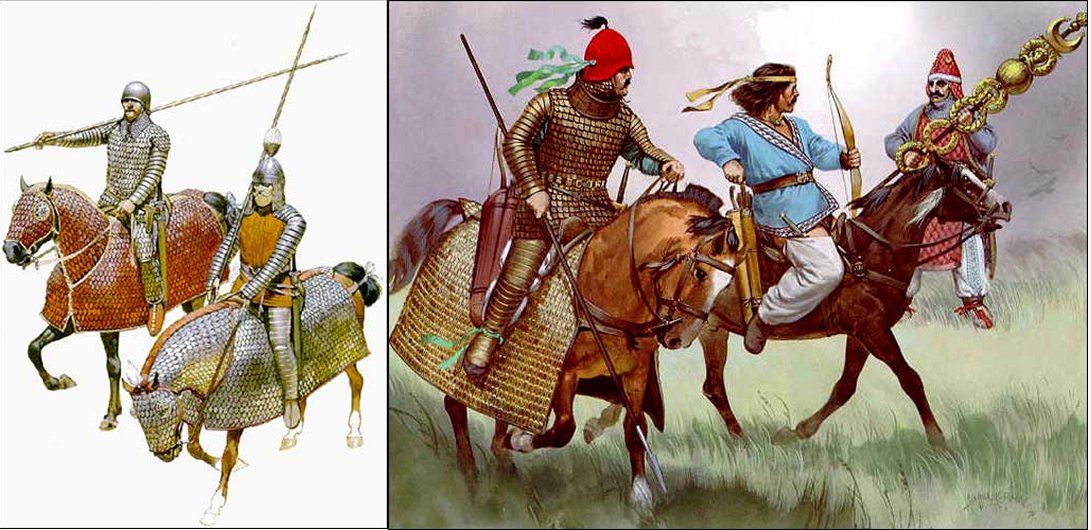

Left: Parthian Cataphracts (Fully Armoured Parthian Cavalry); Right from Left: East Parthian Cataphract (heavy cavalry with man and horse decked in mailed armor.); Middle: Parthian Horse-Archer; Right: Parthian Cataphract from Hatra. Image credit: www.iranchamber.com
The Parthians were originally part of a tribe known as the Parni (or Aparni), who originated on the eastern edge of the Caspian Sea. We know about their history but only from Greek and Roman sources, which mainly describe the Roman battles with the Parthians and their excellent warfare.
The Parthians were literate people but unfortunately, they did not record histories of their dynasty. They built temples, monuments, tombs, and Parthian coins, which they made for the reigns of their kings and this procedure – although, rather unusual in Antiquity – functioned very well.
Their religion was an early form of Zoroastrianism, but they were also tolerant of other religious beliefs.
 The silver drachma of Arsaces I of Parthia (r. c. 247–211 BC) with a Greek-alphabet inscription of his name. Image - Classical Numismatic Group, Inc. http://www.cngcoins.com - CC BY-SA 3.0
The silver drachma of Arsaces I of Parthia (r. c. 247–211 BC) with a Greek-alphabet inscription of his name. Image - Classical Numismatic Group, Inc. http://www.cngcoins.com - CC BY-SA 3.0
Their most famous towns such as Ctesiphon, Seleucia, Ecbatana, Rhagae, Hecatompylus, Nisâ, and Susa flourished. The first king of the Parthians was Tiridates' brother Arsaces I. His capital was Hecatompylus, the capital of the Parthian Arsacid dynasty by 200 BC.
The Parthians, like their neighbors, the Scythians, were able to succeed in battle often due to their use of horse archers. Ancient Parthians were brave and extremely skilled archers mounted on light horses. While pretending to flee at a full gallop in panic, they turned their bodies back to shoot at the pursuing enemy. It was their strategy - to confuse the enemy by pretending to be in retreat – and then, attack.
 A rock-carved relief of Mithridates I of Parthia (r. c. 171–138 BC), seen riding on horseback at Xong-e Ashdar,city of Izeh, Khuzestan Province, Iran. Image: https://iranontrip.ir/page/en-637/Parthian-Empire
A rock-carved relief of Mithridates I of Parthia (r. c. 171–138 BC), seen riding on horseback at Xong-e Ashdar,city of Izeh, Khuzestan Province, Iran. Image: https://iranontrip.ir/page/en-637/Parthian-Empire
From this ancient Parthian strategy originates the term "Parthian shot" that symbolizes perfection and deadly accuracy. Now it is known as “parting shot”.
The key to their many victories was the crucial role of Parthian archers.
The Roman-Parthian wars lasted so long because the Parthians were hard to defeat. The Romans relied on heavy infantry; the Parthian armies contained of two types of cavalry: the heavy-armed and armored cataphracts and light brigades of mounted archers.
Written by – A. Sutherland AncientPages.com Staff Writer
Updated on Oct 14, 2023
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
Expand for referencesReferences:
More From Ancient Pages
-
 Investigation Of The Elusive Will-o’-the-Wisp Leads To A Surprising Discovery
Featured Stories | Feb 6, 2025
Investigation Of The Elusive Will-o’-the-Wisp Leads To A Surprising Discovery
Featured Stories | Feb 6, 2025 -
 Sogdian Temple Of Jartepa II On Caravan Road Of The Silk Road
News | Sep 3, 2020
Sogdian Temple Of Jartepa II On Caravan Road Of The Silk Road
News | Sep 3, 2020 -
 Extraordinary Ancient Roman Ceremonial Chariot Discovered In Pompeii – It’s Still Almost Intact
Archaeology | Mar 1, 2021
Extraordinary Ancient Roman Ceremonial Chariot Discovered In Pompeii – It’s Still Almost Intact
Archaeology | Mar 1, 2021 -
 Neanderthals Had More Children And Lived In Smaller Groups Than Was Previously Thought
Archaeology | May 28, 2019
Neanderthals Had More Children And Lived In Smaller Groups Than Was Previously Thought
Archaeology | May 28, 2019 -
 Earliest Known Abecedary Engraved On Shard Of Pottery Dated To 15th Century BC – Deciphered
Archaeology | Oct 23, 2015
Earliest Known Abecedary Engraved On Shard Of Pottery Dated To 15th Century BC – Deciphered
Archaeology | Oct 23, 2015 -
 Archaeologists Uncover A 20,000-Year-Old Secret That Rewrites The Ancient History Of North America Forever
Featured Stories | Oct 10, 2025
Archaeologists Uncover A 20,000-Year-Old Secret That Rewrites The Ancient History Of North America Forever
Featured Stories | Oct 10, 2025 -
 4,500-Year-Old Ramp Might Explain How Huge Stones Were Transported To Great Pyramids’ Building Site
Archaeology | Nov 9, 2018
4,500-Year-Old Ramp Might Explain How Huge Stones Were Transported To Great Pyramids’ Building Site
Archaeology | Nov 9, 2018 -
 Genuine Bronze Warrior Statuette Unearthed At Technologically Advanced Celtic Settlement Oppidum Of Manching
Archaeology | Aug 18, 2025
Genuine Bronze Warrior Statuette Unearthed At Technologically Advanced Celtic Settlement Oppidum Of Manching
Archaeology | Aug 18, 2025 -
 Rare 4,000-Year-Old Sauna Discovered In Scotland
Archaeology | Oct 3, 2015
Rare 4,000-Year-Old Sauna Discovered In Scotland
Archaeology | Oct 3, 2015 -
 Mediterranean Migration Was Low Over 8,000 Years – New Study
Archaeology | Mar 3, 2021
Mediterranean Migration Was Low Over 8,000 Years – New Study
Archaeology | Mar 3, 2021 -
 Intriguing Discovery Could Offer Proof Of The Tabernacle – Has The Dwelling Place Of God Been Located?
Archaeology | Nov 9, 2013
Intriguing Discovery Could Offer Proof Of The Tabernacle – Has The Dwelling Place Of God Been Located?
Archaeology | Nov 9, 2013 -
 Abu Dhabi Fossil Dunes May Have Inspired The Ancient Great Flood Story – Professor Says
Archaeology | Jul 10, 2022
Abu Dhabi Fossil Dunes May Have Inspired The Ancient Great Flood Story – Professor Says
Archaeology | Jul 10, 2022 -
 Etruscan Beautiful Bronze Lamp of Cortona – Studied
Artifacts | Apr 10, 2024
Etruscan Beautiful Bronze Lamp of Cortona – Studied
Artifacts | Apr 10, 2024 -
 Thor’s Hammer Pendant Found In Norfolk May Be Linked To The Great Heathen Army
Archaeology | Oct 24, 2023
Thor’s Hammer Pendant Found In Norfolk May Be Linked To The Great Heathen Army
Archaeology | Oct 24, 2023 -
 Ancient Greek Goddesses Aphrodite And Artemis – Rivalry And Conflict Over Prestige Illustrated In Hippolytus By Euripides
Featured Stories | Jun 13, 2018
Ancient Greek Goddesses Aphrodite And Artemis – Rivalry And Conflict Over Prestige Illustrated In Hippolytus By Euripides
Featured Stories | Jun 13, 2018 -
 2,000-Year-Old Ruins In Mary Magdalene’s Town Of Magdala On The Shore Of The Sea Of Galilee
Biblical Mysteries | Dec 26, 2014
2,000-Year-Old Ruins In Mary Magdalene’s Town Of Magdala On The Shore Of The Sea Of Galilee
Biblical Mysteries | Dec 26, 2014 -
 New Light On Prehistoric Chalk Plaques From Stonehenge Using Innovative Technology
Archaeology | Nov 3, 2021
New Light On Prehistoric Chalk Plaques From Stonehenge Using Innovative Technology
Archaeology | Nov 3, 2021 -
 Unexpected Neanderthal Behavior In Spain’s Southern Pyrenees – Revealed
Archaeology | Aug 14, 2024
Unexpected Neanderthal Behavior In Spain’s Southern Pyrenees – Revealed
Archaeology | Aug 14, 2024 -
 Why Were These People Buried In A Remote, Unmarked Grave In New Hampshire In The Mid-1800s?
Archaeology | Nov 4, 2024
Why Were These People Buried In A Remote, Unmarked Grave In New Hampshire In The Mid-1800s?
Archaeology | Nov 4, 2024 -
 Rapa Nui’s Population: Growth And Decline – Lesson For Our Future?
Archaeology | Sep 4, 2020
Rapa Nui’s Population: Growth And Decline – Lesson For Our Future?
Archaeology | Sep 4, 2020

