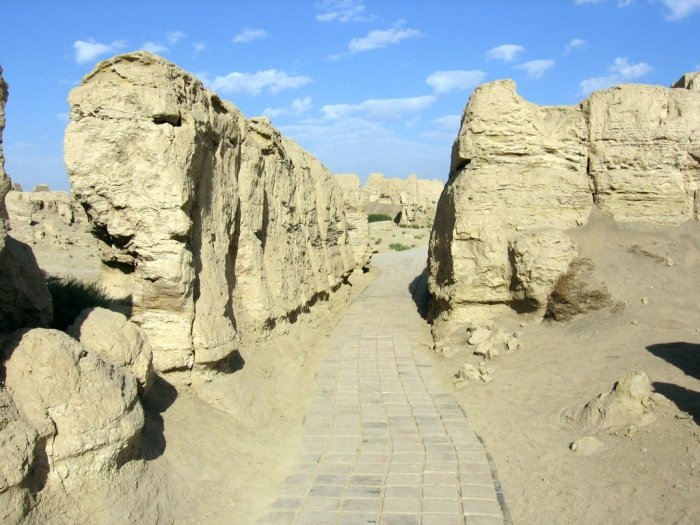
Ruins Of 2,300-Year-Old City Of Jiaohe On The Silk Road
A. Sutherland - AncientPages.com - Jiaohe (in Chinese: 'where two rivers meet') is considered one of China's oldest, largest, and best-preserved earthen cities.
It was built 2,300 years ago, and its ruins are located along the Silk Road in the Yaernaizi Valley, 10 kilometers (6.2 miles) west of Turpan in Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, China.
 Ruins of Jiaohe, a city where all the buildings were dug from earth and wood was rarely used. Credits: China Tour Guide
Ruins of Jiaohe, a city where all the buildings were dug from earth and wood was rarely used. Credits: China Tour Guide
As wood was rarely used, all its buildings were constructed from the earth. People dug houses and rooms downward from the ground and built them with dried bricks.
Jiaohe's main street was long and went down to the center of the islet (1650 m in length, 300 m wide), dividing the city into two parts. The western part was for ordinary people, and the rulers lived in the east. In the northwestern part of the city is a Buddhist monastery, and around China's oldest Buddhist stupa, there are 25 smaller stupas built in all directions.
 Buddhist stupa at Jiaohe Ruins. Photo: commons.Wikimedia
Buddhist stupa at Jiaohe Ruins. Photo: commons.Wikimedia
Jiaohe, which covered 220,000 square meters (2,368,168 square feet), was not like many other ancient cities.
First, it had only two city gates; the South Gate was the main one and vanished long ago, and the East Gate was cut from the side of the cliff, and a few remnants are still recognizable today.
No house gates faced the streets; military defense was seemingly the highest priority for this desert military town with a stronghold from 1,600 years ago.
Turfán (Turpan/Tulufán) es una ciudad-oasis en la Región Autónoma Uigur de Xinjiang en la República Popular China. Ruinas de la antigua ciudad de Jiaohe. Image credit: Colegota - CC BY-SA 2.5 ES
According to Tang dynasty records, Jiaohe had a population of 7,000. Second, typical city walls that usually surround other ancient cities were never found in the town; instead, Jiaohe faced cliffs on three sides.
Both excavations and historical records reveal evidence that Jiaohe (or 'Yarkhoto') was a flourishing ancient trading center and Jiaohe's military importance.
Sir Marc Aurel Stein (1862 - 1943) was a British archeologist and explorer of the Silk Road who traversed 25,000 miles of central Asia and western China. He suggested that the name 'Yarkhoto' is a combination of Turkic and Mongolian words.
The ancient city of Yar?ol near Turpan in the Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of the People’s Republic of China Image credit: Gregor Kneussel - CC BY-SA 3.0
With a history of more than 2,000 years, Jiaohe Ancient City stands isolated on a 30-meter-high plateau in the Ya'ernaizi Valley, 10 kilometers east of Turpan. The whole city of Jiaohe Ancient City stretches about 1650 meters from south to north and 300 meters from east to west.
The relics, still identifiable in this unique city, originated from Tang Dynasty (618-907) architectural style. According to Tang Dynasty historical records, Jiaohe was the capital of the Jushi Kingdom in 108 BC and remained until 450 AD.
Archaeological excavations revealed traces of the Jushi Kingdom at Jiaohe Valley, shedding more light on the early period of the region.
Later, Jiaohe continued to be an essential site for the Silk Road until it lost importance and was eventually destroyed by Genghis Khan.
Written by – A. Sutherland AncientPages.com Staff Writer
Updated on April 25, 2023
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
Expand for referencesMore From Ancient Pages
-
 Unexplained Phenomenon Of The Dancing Mania That Occurred During The Middle Ages
Featured Stories | Aug 1, 2014
Unexplained Phenomenon Of The Dancing Mania That Occurred During The Middle Ages
Featured Stories | Aug 1, 2014 -
 Water Storage Failure And Short-Lived Koh Ker Capital Of Khmer Empire
Archaeology | Nov 1, 2019
Water Storage Failure And Short-Lived Koh Ker Capital Of Khmer Empire
Archaeology | Nov 1, 2019 -
 Oldest Bead In America Discovered At La Prele Mammoth Site, Wyoming
Archaeology | Feb 13, 2024
Oldest Bead In America Discovered At La Prele Mammoth Site, Wyoming
Archaeology | Feb 13, 2024 -
 Eating And Social Habits Of People In The Balearic Islands 3,000 Years Ago – Reconstructed
Archaeology | Jan 18, 2023
Eating And Social Habits Of People In The Balearic Islands 3,000 Years Ago – Reconstructed
Archaeology | Jan 18, 2023 -
 Rhetorica ad Herennium: Ancient Book That Improves Your Memory Using Method Of Loci – You Can Test It Easily
Featured Stories | Feb 21, 2025
Rhetorica ad Herennium: Ancient Book That Improves Your Memory Using Method Of Loci – You Can Test It Easily
Featured Stories | Feb 21, 2025 -
 On This Day In History: Aztec Calendar Stone Rediscovered – On Dec 17, 1790
News | Dec 17, 2016
On This Day In History: Aztec Calendar Stone Rediscovered – On Dec 17, 1790
News | Dec 17, 2016 -
 New Clues About The Fascinating Ancient Roman City Falerii Novi Revealed By Scientists
Archaeology | Sep 13, 2022
New Clues About The Fascinating Ancient Roman City Falerii Novi Revealed By Scientists
Archaeology | Sep 13, 2022 -
 Mystery How Humans Lost Their Body Hair Solved By Scientists
Archaeology | Jan 4, 2023
Mystery How Humans Lost Their Body Hair Solved By Scientists
Archaeology | Jan 4, 2023 -
 ‘Incredibly Rare’ Roman Tomb Unearthed Near London Bridge Station
Archaeology | Jun 13, 2023
‘Incredibly Rare’ Roman Tomb Unearthed Near London Bridge Station
Archaeology | Jun 13, 2023 -
 Aqrabuamelu – Mysterious Scorpion Men In Babylonian Mythology
Featured Stories | Jan 19, 2016
Aqrabuamelu – Mysterious Scorpion Men In Babylonian Mythology
Featured Stories | Jan 19, 2016 -
 Mysterious Golden Curmsun Disc And Its Connection To King Harald Bluetooth And The Legendary Jomsvikings
Artifacts | Apr 13, 2022
Mysterious Golden Curmsun Disc And Its Connection To King Harald Bluetooth And The Legendary Jomsvikings
Artifacts | Apr 13, 2022 -
 Qanats: Ancient 3,000-Year-Old Underground Irrigation Canals Invented By People Of Persia
Ancient Technology | Jul 13, 2020
Qanats: Ancient 3,000-Year-Old Underground Irrigation Canals Invented By People Of Persia
Ancient Technology | Jul 13, 2020 -
 Drought Encouraged Attila’s Huns To Attack The Roman Empire – New Study
Archaeology | Dec 15, 2022
Drought Encouraged Attila’s Huns To Attack The Roman Empire – New Study
Archaeology | Dec 15, 2022 -
 Evidence Of Dual Mass Extinctions 260 Million Years Ago – Found
Fossils | Apr 10, 2023
Evidence Of Dual Mass Extinctions 260 Million Years Ago – Found
Fossils | Apr 10, 2023 -
 Mystery Of Ancient Carved Shiva Lingas In India And Cambodia
Featured Stories | Oct 12, 2015
Mystery Of Ancient Carved Shiva Lingas In India And Cambodia
Featured Stories | Oct 12, 2015 -
 Viking Cork Settlement Re-Writes Ancient History Of Ireland
Archaeology | Jan 16, 2018
Viking Cork Settlement Re-Writes Ancient History Of Ireland
Archaeology | Jan 16, 2018 -
 Bes: Egypt’s Intriguing Dwarf God Of Music, Warfare And Protector Against Snakes, Misfortune And Evil Spirits
Egyptian Mythology | Jul 31, 2016
Bes: Egypt’s Intriguing Dwarf God Of Music, Warfare And Protector Against Snakes, Misfortune And Evil Spirits
Egyptian Mythology | Jul 31, 2016 -
 Mystery Of The Ancient Reptilian Gods Remains A Complex Subject – Memories Of The Past – Part 1
Ancient Mysteries | Feb 6, 2022
Mystery Of The Ancient Reptilian Gods Remains A Complex Subject – Memories Of The Past – Part 1
Ancient Mysteries | Feb 6, 2022 -
 Ten Ancient Jugs May Reveal The Location Of The Biblical Tabernacle
Archaeology | Jul 21, 2017
Ten Ancient Jugs May Reveal The Location Of The Biblical Tabernacle
Archaeology | Jul 21, 2017 -
 European Medieval Burial Practices Were Different Than Previously Thought
Archaeology | Sep 13, 2021
European Medieval Burial Practices Were Different Than Previously Thought
Archaeology | Sep 13, 2021


