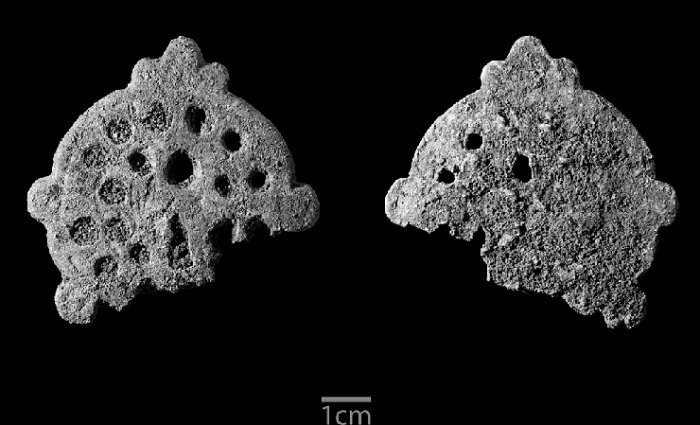
Artifacts And Long History Of Unguja Island – Ancient Humans Impact Island’s Environment
Conny Waters - AncientPages.com - Unguja Ukuu is a small settlement on Unguja island (Zanzibar Island), in Zanzibar, Tanzania.
It is an archaeological site that has yielded abundant artifacts and evidence of the long history of Unguja Ukuu. Artifacts unearthed at Unguja Ukuu came from many places all over the world: pottery from the Far East, Near East, India, and the Southern Mediterranean region.
Other items such as rings, glass, coins, iron artifacts, and ivory have also been found along with a variety of animal remains.
Image credit: Flinders University
Visitors to Unguja Ukuu, centrally located off the east coast of Africa and at the edge of the Indian Ocean, left behind evidence that this place was a central trading port. Unlike the mainland, this site was influenced by foreign merchants and each of them left a mark on this site. Due to the trade activity here early urbanism is evident in one of the first east African trading posts.
Humanity’s impact on the environment is often framed in the context of the post-industrial era but new archaeological research reveals how intensive land use by a medieval East African population altered the natural habitat forever.
Unguja Ukuu, an archaeological settlement located on the Zanzibar Archipelago in Tanzania, was a key port of trade in the Indian Ocean by the first millennium when the island was populated by farming societies establishing trade links toward the Indian Ocean, China, and beyond.
Decorated brass artefact from Unguja Ukuu, Zanzibar (Photo: Ian Cartwright, University of Oxford).
New research published in the Journal of Island and Coastal Archaeology describes how human activities modified the shoreline at Unguja Ukuu.
Urban growth at the coastal settlements and trade ports on the island, and associated trade activities, may have silted up the lagoon hindering the sea traffic and ultimately impacting fish numbers and playing a part in the community’s decline.
For millennia, the Indian Ocean was the maritime setting for a budding form of globalization, with extensive trade and exchange networks operating between Eastern Africa, Southern Arabia, and Southeast Asia which foreshadowed modern global shipping networks.
Image credit: Flinders University
“The islands of the Zanzibar Archipelago witnessed numerous environmental and cultural changes as the region became a hub of maritime trade, cross-cultural interaction, and global exchange,” says the study’s lead author and Senior Lecturer in Archaeology at Flinders University, Dr. Ania Kotarba-Morley.
These changes resulted in the dumping of food remains, general waste, and increased agricultural activity and land use, all of which negatively impacted sediment build-up along the island.
“Whilst discussion about human impacts on the planet and its natural environments is ever-present in our current discourse, they almost always refer to the modern impacts and are focused on agricultural or urban areas such as large cities.
“Our study outlines clearly how human interference in a natural environment impacted coastal landforms and sediments on a remote East African island already over 1000 years ago and directly changed the fortunes of the coastal inhabitants in the area as a result,” says a senior author of the study Associate Professor Mike Morley of Flinders University
Written by Conny Waters - AncientPages.com Staff Writer
More From Ancient Pages
-
 1,400-Year-Old Christian Chalice With Etched Symbols Found In Rubble At Vindolanda Fort, Britain
Artifacts | Sep 1, 2020
1,400-Year-Old Christian Chalice With Etched Symbols Found In Rubble At Vindolanda Fort, Britain
Artifacts | Sep 1, 2020 -
 Suprisingly Huge Ancient Shoe Found Near Hadrian’s Wall May Have Belonged To One Of The Tallest Roman Warriors In Britain
Archaeology | Jun 13, 2025
Suprisingly Huge Ancient Shoe Found Near Hadrian’s Wall May Have Belonged To One Of The Tallest Roman Warriors In Britain
Archaeology | Jun 13, 2025 -
 Could Vancouver Island’s Hepburn Stone Be 15,000 Years Old?
Artifacts | Feb 20, 2021
Could Vancouver Island’s Hepburn Stone Be 15,000 Years Old?
Artifacts | Feb 20, 2021 -
 New Video Footage Reveals Intriguing Viking-Style Shipwreck At The Bottom Of Norway’s Largest Lake Mjøsa
Archaeology | May 5, 2023
New Video Footage Reveals Intriguing Viking-Style Shipwreck At The Bottom Of Norway’s Largest Lake Mjøsa
Archaeology | May 5, 2023 -
 The Parthenon Marbles Evoke Particularly Fierce Repatriation Debates – An Archaeologist Explains Why
Artifacts | Jul 1, 2024
The Parthenon Marbles Evoke Particularly Fierce Repatriation Debates – An Archaeologist Explains Why
Artifacts | Jul 1, 2024 -
 Mystery Of Ancient New York Giants – Who Was Really Buried In The Druid Barrow?
Ancient Mysteries | Oct 28, 2017
Mystery Of Ancient New York Giants – Who Was Really Buried In The Druid Barrow?
Ancient Mysteries | Oct 28, 2017 -
 Unexplained 17th Century Encounters With A Malevolent Entity That Defy Rational Explanation
Featured Stories | May 13, 2025
Unexplained 17th Century Encounters With A Malevolent Entity That Defy Rational Explanation
Featured Stories | May 13, 2025 -
 Remarkable Discovery Of Ancient Drilled Bear Teeth In Kansas – How Did They End Up On The Great Plains?
Archaeology | Mar 25, 2022
Remarkable Discovery Of Ancient Drilled Bear Teeth In Kansas – How Did They End Up On The Great Plains?
Archaeology | Mar 25, 2022 -
 Easter Island’s Moai Statues Did ‘Walk,’ Researchers Demonstrate Using Physics And 3D Modeling
Archaeology | Oct 8, 2025
Easter Island’s Moai Statues Did ‘Walk,’ Researchers Demonstrate Using Physics And 3D Modeling
Archaeology | Oct 8, 2025 -
 Ancient Codex Cospi: Intriguing Pre-Columbian Ritual Manuscript From Central Mexico
Featured Stories | Aug 10, 2017
Ancient Codex Cospi: Intriguing Pre-Columbian Ritual Manuscript From Central Mexico
Featured Stories | Aug 10, 2017 -
 Why Do Some Men Think Often About The Roman Empire?
News | Oct 4, 2023
Why Do Some Men Think Often About The Roman Empire?
News | Oct 4, 2023 -
 Remains Of Ancient Roman Military Camp Discovered In Brno, Czech Republic
Archaeology | Jan 26, 2018
Remains Of Ancient Roman Military Camp Discovered In Brno, Czech Republic
Archaeology | Jan 26, 2018 -
 Unique 4,000-Year-Old Board Game – Unearthed In Oman
Archaeology | Jan 18, 2022
Unique 4,000-Year-Old Board Game – Unearthed In Oman
Archaeology | Jan 18, 2022 -
 125,000 Years Ago Neanderthals Hunted Elephants Much Larger Than Extinct Woolly Mammoths
Archaeology | Dec 5, 2023
125,000 Years Ago Neanderthals Hunted Elephants Much Larger Than Extinct Woolly Mammoths
Archaeology | Dec 5, 2023 -
 ‘Empty’ Egyptian Coffin Kept In Museum Contained A 2,500-Year-Old Mummy
Archaeology | Mar 31, 2018
‘Empty’ Egyptian Coffin Kept In Museum Contained A 2,500-Year-Old Mummy
Archaeology | Mar 31, 2018 -
 A 17th-Century Warship Blekinge Was Deliberately Sunk During Sweden’s War With Russia And Its Allies
Archaeology | Feb 2, 2017
A 17th-Century Warship Blekinge Was Deliberately Sunk During Sweden’s War With Russia And Its Allies
Archaeology | Feb 2, 2017 -
 Unknown Prehistoric Henge Site Detected Near Famous Newgrange In Ireland’s East Coast
Archaeology | Jul 13, 2018
Unknown Prehistoric Henge Site Detected Near Famous Newgrange In Ireland’s East Coast
Archaeology | Jul 13, 2018 -
 Nygrotta: Species Migration Occurred Due To Climatic Shifts Millennia Ago – Ancient DNA And Bones Show
Paleontology | Apr 5, 2024
Nygrotta: Species Migration Occurred Due To Climatic Shifts Millennia Ago – Ancient DNA And Bones Show
Paleontology | Apr 5, 2024 -
 Jomon Period: Triangle-Shaped Stone Artifact Depicting Human Face Found For The First Time In Japan
Archaeology | Dec 25, 2017
Jomon Period: Triangle-Shaped Stone Artifact Depicting Human Face Found For The First Time In Japan
Archaeology | Dec 25, 2017 -
 Ancient City Of Uxmal And Magnificent Pyramid Of The Magician
Featured Stories | Dec 19, 2015
Ancient City Of Uxmal And Magnificent Pyramid Of The Magician
Featured Stories | Dec 19, 2015



