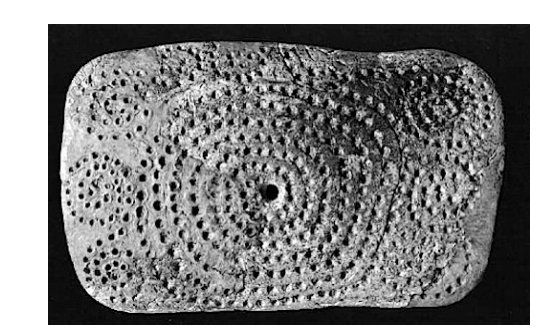
Astonishing Lunar And Solar Calendars Created 30,000 B.C.
Ellen Lloyd - AncientPages.com - At first glance, these ancient artifacts may look like ordinary bones covered with insignificant dots. That is not the case, however.
Closer examination of carved-engraved bone plates discovered in France has revealed people created astonishing lunar and solar calendars 30,000 B.C.
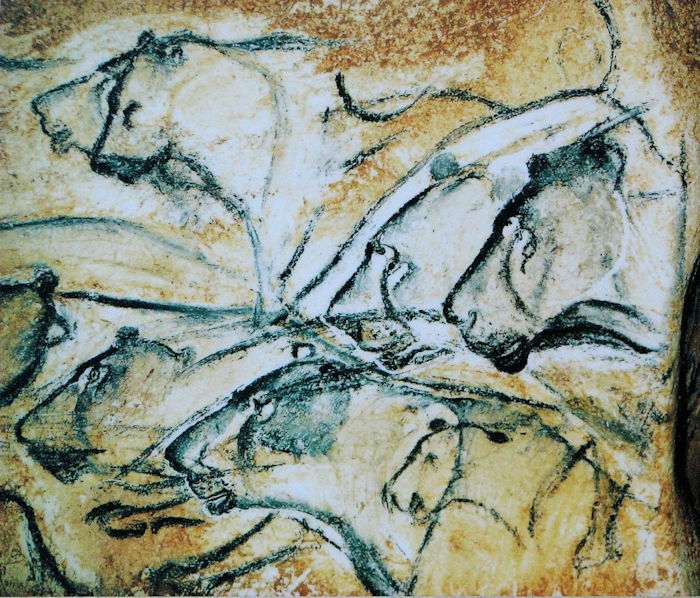
Chauvet-Pont d'Arc cave replica, the lions "fresco". Credit: HTO - Public Domain
For as long as anyone can remember, people have been fascinated with the night skies. There are many examples of how our ancestors’ profound interest in astronomy.
Observations of celestial objects took place in many prehistoric societies. Today, we can admit that ancient astronomers possessed advanced knowledge about the Sun, the Moon, asteroids, various solar planets, and interesting cosmic events. When and where people started to study the heavens and celestial objects is impossible to say, but if we turn our attention to Europe, we discover something quite extraordinary.
European Paleolithic works of art can be dated to approximately 30 000 BC. and are considered one of the achievements of the Upper Paleolithic cognitive revolution. The earliest cave paintings in La Grotte Chauvet-Pont-d’Arc, France were created about 31 000 years ago. Not only are the images a great example of prehistoric art, but they have also motivated researchers to attempt to “decipher” the meaning and purpose behind some of the ancient symbols.
While examining Paleolithic cave art scientists discovered that Paleolithic people had a great interest in astronomy.
Alexander Marshack (1918-2004), an American independent scholar and Paleolithic archaeologist, was one of the first scientists who stated astronomy played an essential role during the Upper-Paleolithic era.
He studied ancient bone fragments discovered in French caves. He interpreted the various Paleolithic and Mesolithic, mostly portable, objects that bear engraved or painted series of dots or lines as accurate lunar observations.
Juan Antonio Belmonte writes in the book Ancient Astronomy: India, Egypt, China, Maya, Inca, Aztec, Greece, Rome, Genesis, Hebrews, Christians, the Neolithic and Paleolithic that Marshack’s “arguments were based not only on counting the signs but on what he called “microscopic analysis.”
The interpretation of the markings on various artifacts as notational systems rests on the hypothesis of a slow accumulation of these marks, which correlates with lunar or solar motion. Thus he concluded that these artifacts reflect nonarithmetic observational astronomical skills and lore. The most well-known depiction interpreted by him is found on the bone plate about 30 000 years old, from Abri Blanchard (Dordogne, France), which is said to represent the waxing and waning moon positions in serpentine form.”
Top: Abri Blanchard, Dordogne, France. Archaeological Museum. Bottom: Cave of Taï, Drôme, France
“Francesco d’Errico and colleagues developed a different type of methodology (d’Errico 1989). Drawing on experimental archaeology, they compiled a database in an attempt to demonstrate whether the notches represent notational systems or not.
After investigating a great number of artifacts they concluded that there were some objects which might have depicted parts of a series of complex codes based on the hierarchical organization of information, and using formally differentiated marks. One of these artifacts might be the find from the cave Taï (Drôme, France) whose age is about 10 000 years.
After studying Eurasian portable art the Russian investigator B.A. Frolov also became convinced that these objects were calendars following the monthly motion of the moon and/or yearly solar path, and claimed they were used by early communities. The most well-known bone plate interpreted as a lunisolar calendar is from Ma’lta (Irkutskaya Oblast, Russia).”
The theory that people created such complex lunar and solar calendars so long ago may sound somewhat far-fetched. Still, there is a lot of evidence that suggests our ancestors were rather familiar with the movements of the Sun, Moon, and even other planets.
Updated on March 22, 2022
Written by Ellen Lloyd – AncientPages.com
Copyright © AncientPages.com All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com
More From Ancient Pages
-
 Spectacular 2,500 Years Old Shwedagon Pagoda In Myanmar – World’s Oldest Pagoda
Featured Stories | Oct 18, 2018
Spectacular 2,500 Years Old Shwedagon Pagoda In Myanmar – World’s Oldest Pagoda
Featured Stories | Oct 18, 2018 -
 Elli – Norse Goddess And Symbol Of Old Age That No One Ever Could Defeat
Featured Stories | Dec 21, 2017
Elli – Norse Goddess And Symbol Of Old Age That No One Ever Could Defeat
Featured Stories | Dec 21, 2017 -
 A Scientific Surprise: Bering Land Bridge Formed Late During Last Ice Age
Archaeology | Dec 27, 2022
A Scientific Surprise: Bering Land Bridge Formed Late During Last Ice Age
Archaeology | Dec 27, 2022 -
 Mysterious Ancient Underground Stone Rings Made By Neanderthals 176,500 Years Ago For Unknown Reasons
Archaeology | May 26, 2016
Mysterious Ancient Underground Stone Rings Made By Neanderthals 176,500 Years Ago For Unknown Reasons
Archaeology | May 26, 2016 -
 Chinese Writing System – Increasingly Complex Over The Course Of Its 3000-Year History
Linguistic Discoveries | Nov 23, 2022
Chinese Writing System – Increasingly Complex Over The Course Of Its 3000-Year History
Linguistic Discoveries | Nov 23, 2022 -
 Relics From Day-To-Day Life At Shakespeare’s Home – Now Shown In New Virtual Exhibition
Archaeology | Dec 11, 2020
Relics From Day-To-Day Life At Shakespeare’s Home – Now Shown In New Virtual Exhibition
Archaeology | Dec 11, 2020 -
 Mystery Of The Watchers And Book Of Enoch – Fallen Angels And Their Secret Knowledge
Biblical Mysteries | Oct 27, 2017
Mystery Of The Watchers And Book Of Enoch – Fallen Angels And Their Secret Knowledge
Biblical Mysteries | Oct 27, 2017 -
 Has World’s Oldest Image Of Virgin Mary Been Discovered In Dura-Europos Church?
Archaeology | Mar 17, 2017
Has World’s Oldest Image Of Virgin Mary Been Discovered In Dura-Europos Church?
Archaeology | Mar 17, 2017 -
 Amaterasu: Shinto Goddess Of The Sun And Priestess-Queen Sister To Controversial Susanoo God Of Storms
Featured Stories | Jan 25, 2019
Amaterasu: Shinto Goddess Of The Sun And Priestess-Queen Sister To Controversial Susanoo God Of Storms
Featured Stories | Jan 25, 2019 -
 Mysterious Yamacutah – A Sacred Native American Indian Shrine
Artifacts | Sep 18, 2020
Mysterious Yamacutah – A Sacred Native American Indian Shrine
Artifacts | Sep 18, 2020 -
 Ancient Monuments The World Is Not Allowed To See – Forbidden Zone – Part 2
Featured Stories | Aug 27, 2020
Ancient Monuments The World Is Not Allowed To See – Forbidden Zone – Part 2
Featured Stories | Aug 27, 2020 -
 Dunino Den: Mysterious And Sacred Ancient Site In Scotland With Enigmatic Rock Faces And Symbols
Featured Stories | Jan 6, 2017
Dunino Den: Mysterious And Sacred Ancient Site In Scotland With Enigmatic Rock Faces And Symbols
Featured Stories | Jan 6, 2017 -
 3,000-Year-Old Stone Scarab Seal Depicting A Pharaoh Discovered In Israel
Archaeology | Dec 2, 2022
3,000-Year-Old Stone Scarab Seal Depicting A Pharaoh Discovered In Israel
Archaeology | Dec 2, 2022 -
 Ancient DNA Yields Surprising Findings On World’s Earliest Seafarers
Archaeology | Jun 30, 2022
Ancient DNA Yields Surprising Findings On World’s Earliest Seafarers
Archaeology | Jun 30, 2022 -
 Birds – Mysterious Avian Messengers That Symbolized Bridge Between Humans And Gods In World Beliefs
Featured Stories | Aug 21, 2021
Birds – Mysterious Avian Messengers That Symbolized Bridge Between Humans And Gods In World Beliefs
Featured Stories | Aug 21, 2021 -
 Ancient Stela Of Piankhi – King Of Napata, Rightful Ruler And Maintainer Of Maat
Featured Stories | Apr 25, 2018
Ancient Stela Of Piankhi – King Of Napata, Rightful Ruler And Maintainer Of Maat
Featured Stories | Apr 25, 2018 -
 Unexpected Discovery Of Viking Trading Place In Norway Re-Writes History
Archaeology | Jul 22, 2020
Unexpected Discovery Of Viking Trading Place In Norway Re-Writes History
Archaeology | Jul 22, 2020 -
 What Is The History Of Pancakes?
Ancient History Facts | Mar 7, 2024
What Is The History Of Pancakes?
Ancient History Facts | Mar 7, 2024 -
 Yuki-Onna ‘Lady Of The Snow’: A Female Demon And Symbol Of Death In Japanese Mythology
Featured Stories | Mar 7, 2019
Yuki-Onna ‘Lady Of The Snow’: A Female Demon And Symbol Of Death In Japanese Mythology
Featured Stories | Mar 7, 2019 -
 One Of The Biggest Gold Treasures Ever Discovered In Denmark Is 1,500-Year-Old
Archaeology | Sep 6, 2021
One Of The Biggest Gold Treasures Ever Discovered In Denmark Is 1,500-Year-Old
Archaeology | Sep 6, 2021