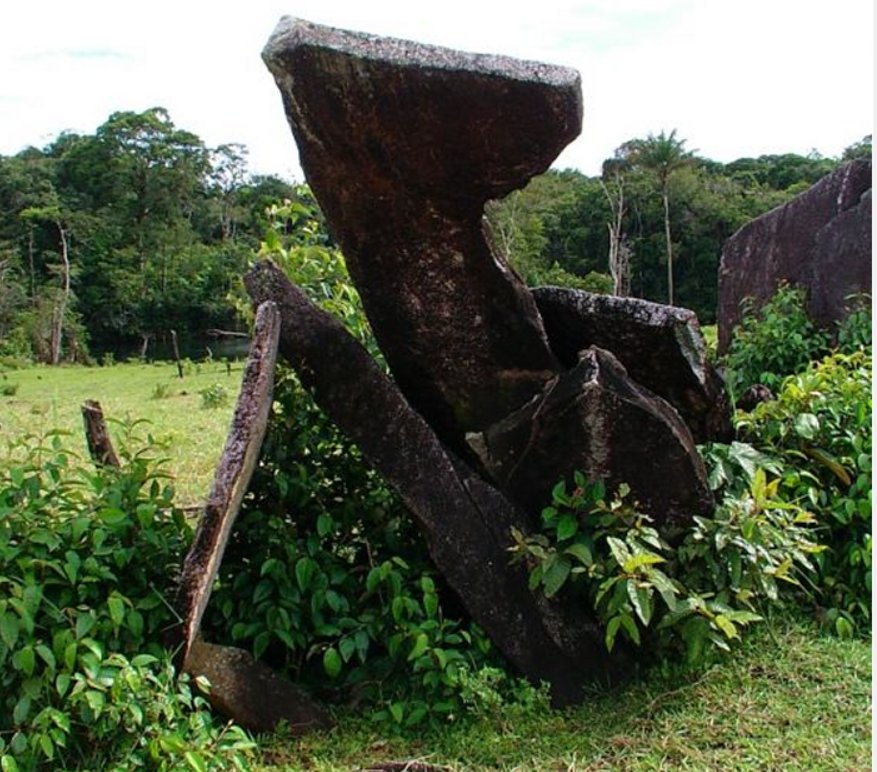
Calçoene – Amazon Stonehenge And The Mysterious Amapán Megalithic Culture
Ellen Lloyd - AncientPages.com - In the distant past, people in Brazil raised fascinating megalithic structures still shrouded in mystery. One intriguing monument is Calçoene, also called the Amazon Stonehenge.
The Calzoene's 'Stonehenge' - Image credit: Leandroisola - CC BY-SA 4.0 DEED
The true purpose of this structure remains to be discovered. It could have been used as an ancient astronomical observatory or for burial purposes, or perhaps both.
Discovery Of The Amazon Stonehenge
Megalithic structures in Amapá state, Brazil, near the city of Calçoene, were first reported by naturalist Emilio Goeldi. While exploring the region, he noticed settings of upright stones in the late 19th century.
At this site, archaeologists have uncovered several fascinating artifacts that could shed more light on the mysterious Amapán people.
The Amazon Stonehenge, sometimes called the "Tropical Stonehenge," raises many baffling questions. 2005 Archaeologists began excavating the site in 2005, but a thorough study of the megalithic structures has yet to be conducted.
So far, 20 megalithic structures, eight burial caves, a mound, and some ancient villages have been discovered.
Calçoene Megalithic Structures Reveal Evidence Of Ancient Astronomical Knowledge
For the most part, Amapán megaliths are easily visible and located on the tops of hills. The stones vary much in size. The megaliths consist of upright or slanted granite blocks in circular arrangements. Some circles are small, less than 10 m in diameter.
A megalithic stone circle in Calçoene, Brazil. The site also called the Amazon Stonehenge.The largest stone structure has a diameter of more than 30 m. The granite stones are rough and straightforward. Image source: Wikipedia commons.
The stones have yet to be submitted to dating techniques, but the carbon-dating of unearthed pottery suggests the site is between 500-2,000 years old.
Studies of the Amazon Stonehenge reveal a connection between the stone structures and the Amapá culture's interest in astronomy. The Stonehenge comparison with the Amazon discovery is due to the astronomical significance of both sites.
On the winter solstice of December 21, the shortest day of the year in the northern hemisphere, the shadow of one of the blocks disappears when the sun is directly above it. The rock has been placed at an angle so that the shadow is possibly tiny throughout the day. This particular block's alignment with the December solstice leads archaeologists to consider the possibility that the site was once an astronomical observatory. During the winter solstice, the sun shines directly through this hole onto another rock for an extended time.
If the stone structure served as a megalithic observatory, then it must have been constructed by sophisticated indigenous culture.
Many of the world's indigenous peoples are thought to use the symbolism of the sky on Earth to harness the power of the celestial world. It would seem that the Amapá megalithic culture was also fascinated with the night sky and heavenly bodies.
The Amazon Stonehenge could re-write the ancient history of ancient societies in South America. Therefore, the stone circles must be studied in more detail. Scientific examinations of the archaeological sites can provide us with more clues and hopefully answers as to the age of the Amapán megalithic culture and its mysterious disappearance.
Written by Ellen Lloyd – AncientPages.com
Updated on January 16, 2024
Copyright © AncientPages.com & Ellen Lloyd All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed in whole or part without the express written permission of AncientPages.com and Ellen Lloyd
More From Ancient Pages
-
 Tarascan Indians: Intriguing Pre-Columbian Civilization Of Artists, Warriors And Skilled Metallurgists
Civilizations | Sep 9, 2021
Tarascan Indians: Intriguing Pre-Columbian Civilization Of Artists, Warriors And Skilled Metallurgists
Civilizations | Sep 9, 2021 -
 Roman Treasures Unearthed At Ancient Site Of Tiel, Netherlands
Archaeology | Apr 2, 2017
Roman Treasures Unearthed At Ancient Site Of Tiel, Netherlands
Archaeology | Apr 2, 2017 -
 3,500-Year-Old Cuneiform Clay Tablets With Hittites’ Texts – Soon To Be Accessible Online
News | Oct 15, 2020
3,500-Year-Old Cuneiform Clay Tablets With Hittites’ Texts – Soon To Be Accessible Online
News | Oct 15, 2020 -
 On This Day In History: Ferdinand Magellan Reached Pacific And South American Strait – On Nov 28, 1520
News | Nov 28, 2016
On This Day In History: Ferdinand Magellan Reached Pacific And South American Strait – On Nov 28, 1520
News | Nov 28, 2016 -
 Alexander The Great And The Prophecy Of The Tree Of The Sun And Moon
Featured Stories | Jun 10, 2019
Alexander The Great And The Prophecy Of The Tree Of The Sun And Moon
Featured Stories | Jun 10, 2019 -
 What Was It Like To Be A Student In The Middle Ages?
Ancient History Facts | Jun 6, 2019
What Was It Like To Be A Student In The Middle Ages?
Ancient History Facts | Jun 6, 2019 -
 LIDAR Images Reveal Cambodia’s Greater Angkor Region Was Home To 700,000-900,000 People
Archaeology | May 8, 2021
LIDAR Images Reveal Cambodia’s Greater Angkor Region Was Home To 700,000-900,000 People
Archaeology | May 8, 2021 -
 Tile Tomb Dated To The Late Hellenistic Era – Discovered In Surroundings Of Istanbul, Turkey
Archaeology | Jun 6, 2022
Tile Tomb Dated To The Late Hellenistic Era – Discovered In Surroundings Of Istanbul, Turkey
Archaeology | Jun 6, 2022 -
 What Routes Did Homo Sapiens Take On His Way From Africa To Europe And Asia? Out Of Africa Path Examined
Archaeology | Dec 26, 2021
What Routes Did Homo Sapiens Take On His Way From Africa To Europe And Asia? Out Of Africa Path Examined
Archaeology | Dec 26, 2021 -
 Ancient Greeks Invented Alarm Clocks
Ancient History Facts | May 6, 2016
Ancient Greeks Invented Alarm Clocks
Ancient History Facts | May 6, 2016 -
 10 Great Ancient Mysteries Of North America
Featured Stories | Sep 30, 2015
10 Great Ancient Mysteries Of North America
Featured Stories | Sep 30, 2015 -
 Mystery Of Great Wall Of California: An Ancient Unsolved Enigma
Featured Stories | Oct 28, 2015
Mystery Of Great Wall Of California: An Ancient Unsolved Enigma
Featured Stories | Oct 28, 2015 -
 Mystery Of Dakhamunzu And The Zannanza Affair – Was Queen Ankhesenamun Hiding Her Identity?
Featured Stories | Feb 1, 2019
Mystery Of Dakhamunzu And The Zannanza Affair – Was Queen Ankhesenamun Hiding Her Identity?
Featured Stories | Feb 1, 2019 -
 Major Archaeological Discovery Of A 7,000-Year-Old Settlement In Miami – But Its Future Is In Danger
Archaeology | Feb 10, 2023
Major Archaeological Discovery Of A 7,000-Year-Old Settlement In Miami – But Its Future Is In Danger
Archaeology | Feb 10, 2023 -
 Viking Women Were More Prominent Than Previously Thought – Archaeological Discoveries Reveal
Archaeology | Sep 6, 2019
Viking Women Were More Prominent Than Previously Thought – Archaeological Discoveries Reveal
Archaeology | Sep 6, 2019 -
 What Were Victorian Bathing Machines?
Ancient History Facts | Jun 9, 2018
What Were Victorian Bathing Machines?
Ancient History Facts | Jun 9, 2018 -
 Unexplained Phenomenon In East Anglia – Time Portal And Strange Glimpses From The Past – Part 1
Featured Stories | May 31, 2018
Unexplained Phenomenon In East Anglia – Time Portal And Strange Glimpses From The Past – Part 1
Featured Stories | May 31, 2018 -
 On This Day In History: Antarctic Explorer Lawrence “Titus” Oates Born – On Mar 17, 1880
News | Mar 17, 2017
On This Day In History: Antarctic Explorer Lawrence “Titus” Oates Born – On Mar 17, 1880
News | Mar 17, 2017 -
 Small Stone Carved With A Viking Ship May Be Oldest Picture Ever Found In Iceland
Archaeology | Jun 16, 2023
Small Stone Carved With A Viking Ship May Be Oldest Picture Ever Found In Iceland
Archaeology | Jun 16, 2023 -
 How Did Sargon Become The Most Powerful Ruler Of Mesopotamia?
Featured Stories | Apr 3, 2020
How Did Sargon Become The Most Powerful Ruler Of Mesopotamia?
Featured Stories | Apr 3, 2020


